Render into a framebuffer and use it as a texture.
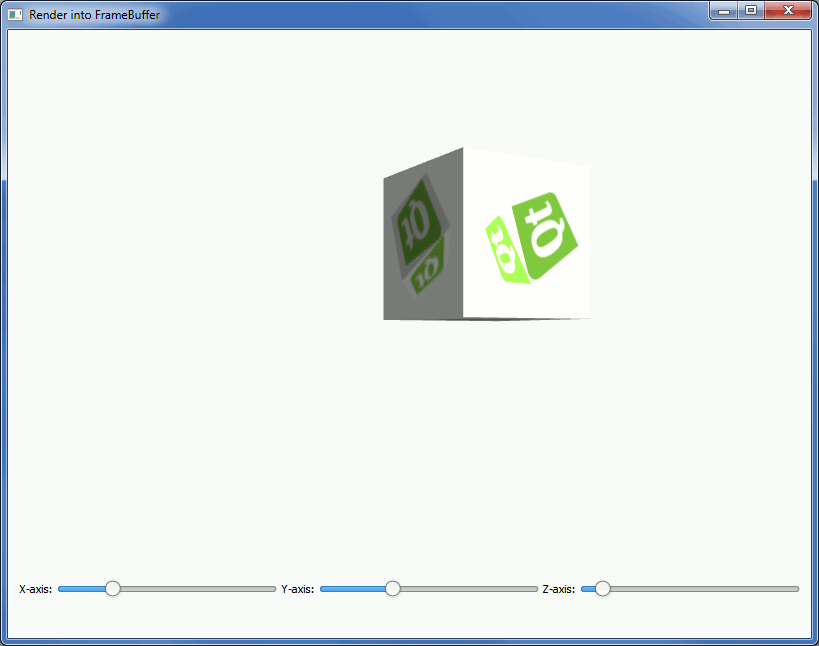
The Framebuffer Example shows how to render into a framebuffer, create a texture of it, and apply the texture to an object in normal on-screen rendering.
The example has a moving and rotating cube, which has another textured cube drawn into it via the framebuffer object. The cube in the framebuffer can be rotated using Slider s from Qt Quick Controls .
We first define the variables we need for the render-to-texture framebuffer:
var rttFramebuffer; var rttTexture; var rttWidth = 512; var rttHeight = 512;
Then, in the
initializeGL
function, we create the framebuffer object:
// Create the framebuffer object rttFramebuffer = gl.createFramebuffer(); rttFramebuffer.name = "OffscreenRenderTarget"; gl.bindFramebuffer(gl.FRAMEBUFFER, rttFramebuffer);
After the creation of the framebuffer, we create the texture:
// Create the texture rttTexture = gl.createTexture(); rttTexture.name = "OffscreenRenderTargetTexture"; gl.bindTexture(gl.TEXTURE_2D, rttTexture); gl.texParameteri(gl.TEXTURE_2D, gl.TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, gl.LINEAR); gl.texParameteri(gl.TEXTURE_2D, gl.TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, gl.LINEAR_MIPMAP_NEAREST); gl.texImage2D(gl.TEXTURE_2D, 0, gl.RGBA, rttWidth, rttHeight, 0, gl.RGBA, gl.UNSIGNED_BYTE, null); gl.generateMipmap(gl.TEXTURE_2D);
Then we need to bind the texture as a color attachment, create and bind a render buffer, and bind the depth attachment:
// Bind the texture as color attachment, create and bind a depth buffer gl.framebufferTexture2D(gl.FRAMEBUFFER, gl.COLOR_ATTACHMENT0, gl.TEXTURE_2D, rttTexture, 0); var renderbuffer = gl.createRenderbuffer(); gl.bindRenderbuffer(gl.RENDERBUFFER, renderbuffer); gl.renderbufferStorage(gl.RENDERBUFFER, gl.DEPTH_COMPONENT16, rttWidth, rttHeight); gl.framebufferRenderbuffer(gl.FRAMEBUFFER, gl.DEPTH_ATTACHMENT, gl.RENDERBUFFER, renderbuffer);
在
paintGL
function, we first need to draw the scene into the framebuffer. We start by binding the framebuffer object and setting a viewport:
// bind the FBO and setup viewport gl.bindFramebuffer(gl.FRAMEBUFFER, rttFramebuffer); gl.viewport(0, 0, rttWidth, rttHeight);
Then, we need to bind the loaded texture we want to use in rendering into the framebuffer object:
// Bind the loaded texture gl.bindTexture(gl.TEXTURE_2D, cubeTexture);
And then we can draw the textured cube into the framebuffer:
// Draw the cube to the FBO gl.drawElements(gl.TRIANGLES, 36, gl.UNSIGNED_SHORT, 0);
First, we bind the render-to-texture right after drawing, and generate mipmaps:
// Bind the render-to-texture and generate mipmaps gl.bindTexture(gl.TEXTURE_2D, rttTexture); gl.generateMipmap(gl.TEXTURE_2D);
Then we need to bind the default framebuffer (screen), and set up the viewport:
// Bind default framebuffer and setup viewport accordingly gl.bindFramebuffer(gl.FRAMEBUFFER, 0); gl.viewport(0, 0, canvas.width * canvas.devicePixelRatio, canvas.height * canvas.devicePixelRatio);
And finally, we draw the on-screen view:
// Draw the on-screen cube gl.drawElements(gl.TRIANGLES, 36, gl.UNSIGNED_SHORT, 0);
文件:
图像: