Demonstrates working with custom Android activities.
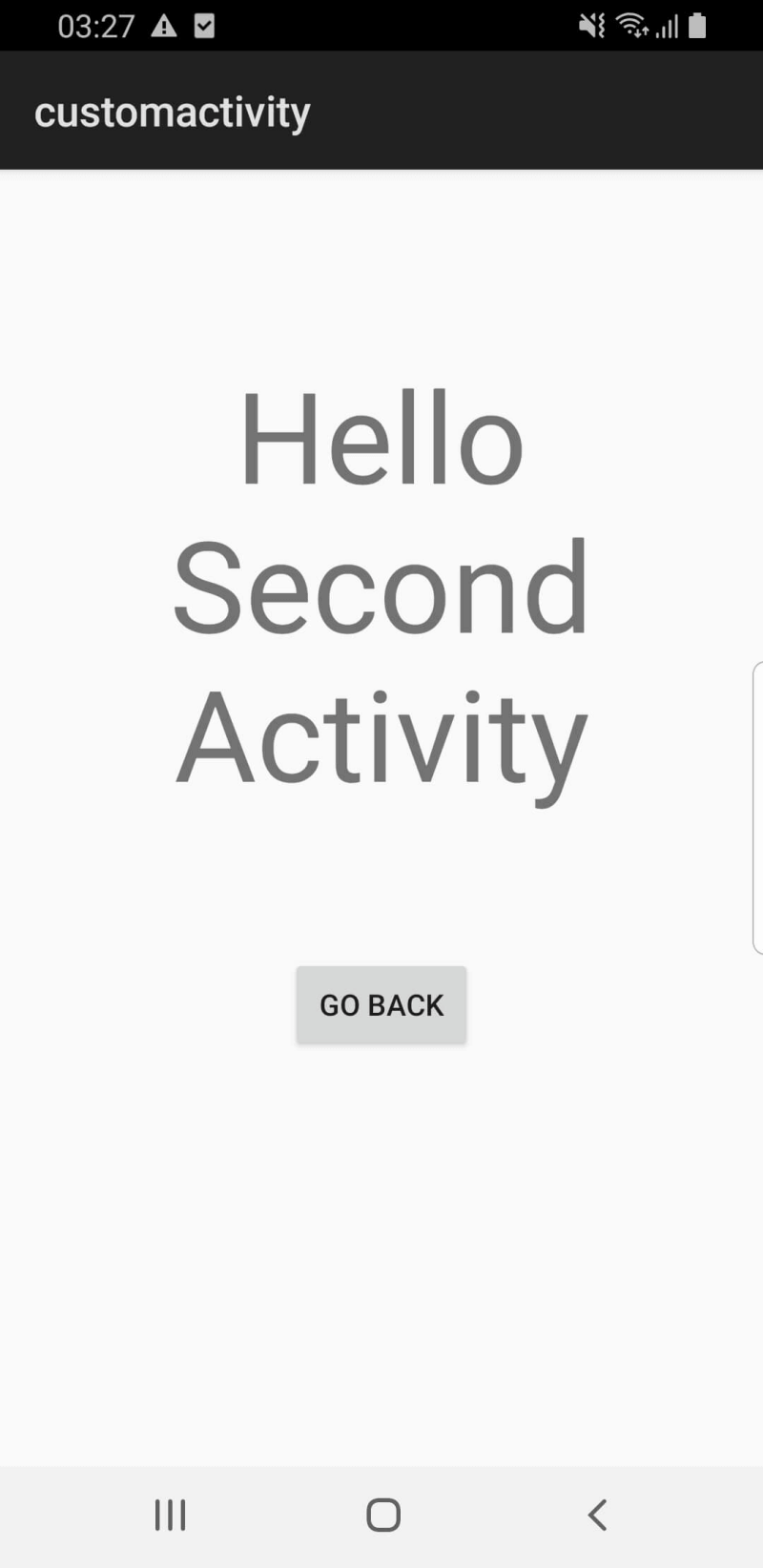
This example demonstrates how to create an Android Activity and run it from your Qt application. The activity is composed of a Java class and an Android XML layout which is started from the main app. The activity can send back data after finishing which can be used in QML.
When you click the "Start custom Android activity" button, the activity is started, and the activity has a text view and a button to exit. The activity can either use the button or the back gesture to go back.
要运行范例从 Qt Creator ,打开 欢迎 模式,然后选择范例从 范例 。更多信息,拜访 构建和运行范例 .
Define an Android class called
CustomActivity
in the CustomActivity.java file as follows:
package org.qtproject.example.activityhandler;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class CustomActivity extends Activity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.second_activity);
Button backButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.backButton);
backButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Intent resultIntent = new Intent();
resultIntent.putExtra("message", "Back button clicked.");
setResult(Activity.RESULT_OK, resultIntent);
finish();
}
});
}
}
The Activity's layout is defined at customactivity/android/res/layout/second_activity.xml .
To use this Activity, it must be defined in the AndroidManifest.xml file as follows:
<activity android:process=":custom_activity" android:name=".CustomActivity" android:label="-- %%INSERT_APP_NAME%% --">
<!-- android:process=":qt" is needed to force the service to run on a separate process than the Activity -->
<meta-data android:name="android.app.lib_name" android:value="-- %%INSERT_APP_LIB_NAME%% --"/>
</activity>
注意:
To use any native JNI calls, you must extend
QtActivity
而不是
Activity
.
To start an Activity from Qt, you need to create an intent using QAndroidIntent , then call QtAndroid::startActivity providing the intent, a custom request code, and a callback function. The latter is called after the activity has finished. You can start the activity as follows:
void ActivityHandler::showSecondActivity() { QAndroidIntent activityIntent(QtAndroid::androidActivity().object(), "org/qtproject/example/activityhandler/CustomActivity"); QtAndroid::startActivity( activityIntent.handle(), REQUEST_CODE, [this](int requestCode, int resultCode, const QAndroidJniObject &data) { activityReceiver(requestCode, resultCode, data); }); }
Then, define the callback function that is called directly after the activity is done:
void ActivityHandler::activityReceiver(int requestCode, int resultCode, const QAndroidJniObject &data) { if (requestCode == REQUEST_CODE) { if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) { const QAndroidJniObject key = QAndroidJniObject::fromString("message"); const QAndroidJniObject message = data.callObjectMethod( "getStringExtra", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/String;", key.object()); if (message.isValid()) emit ActivityHandler::instance()->receiveFromActivityResult(message.toString()); } else {
注意:
You can first check that the
requestCode
and
resultCode
are correct.
To connect C++ with QML, add an instance of the C++ class that is handling the JNI logic as a QML property in the main.cpp 文件:
ActivityHandler *activityHandler = new ActivityHandler(&app);
engine.rootContext()->setContextProperty(QLatin1String("activityHandler"), activityHandler);
Then, add a Connections element to watch for messages from C++ in the main.qml 文件:
Connections {
target: activityHandler
function onReceiveFromActivityResult(message) {
resultText.text = status + message
}
}
And set the
onClicked
为
"Start custom Android activity"
button to:
onClicked: qtAndroidService.sendToService(pingText.text)
另请参阅 Qt for Android and Qt Android Extras .