Demonstrates how to run an Android service in the main process, and how to communicate between QML/C++ and a Java service.
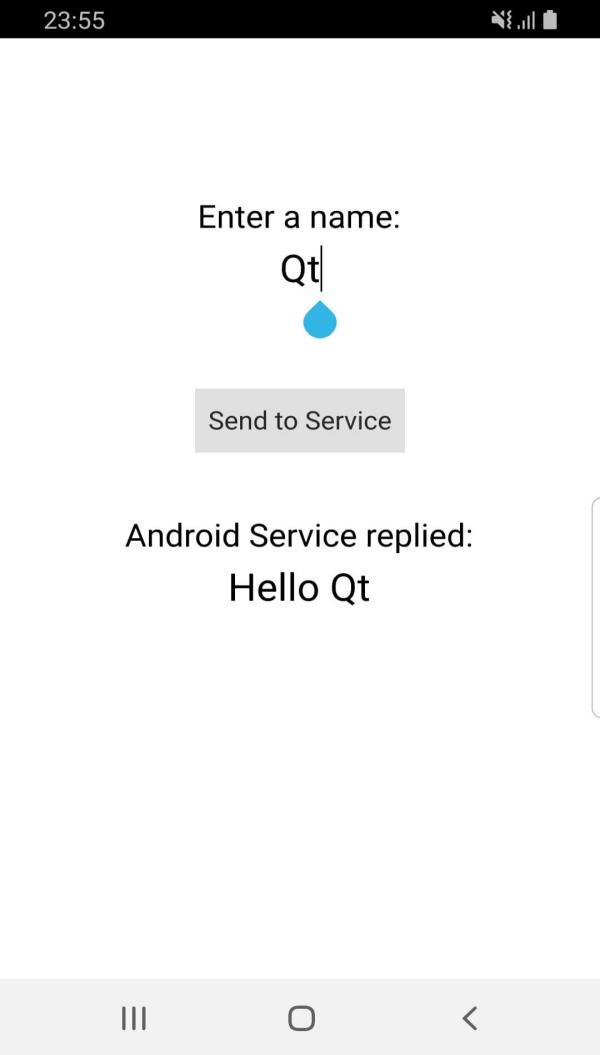
This example demonstrates how to create and run a simple Android service in the same process as the main activity
QtActivity
, and then exchange data between QML/C++ and the Java service. This service is a pure Java implementation.
When clicking the
Send to Service
button, the name entered in the QML view, Qt, in this case, is sent to the Android service. Then, the service replies back with a message
Hello Qt
which is printed in the QML view.
要运行范例从 Qt Creator ,打开 欢迎 模式,然后选择范例从 范例 。更多信息,拜访 构建和运行范例 .
When running the app's process, you can extend either
QtService
or
Service
. Extending
QtService
allows Qt to load all the necessary libraries to load Qt components correctly and call native methods on Android. However, here the service is running in the same process, so extending either class works.
Start by creating the Java service class. This is a normal Android
Service
that receives a name from QML and replies back with
Hello <name>
:
package org.qtproject.example.qtandroidservice;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.util.Log;
import android.app.Service;
import android.os.IBinder;
public class QtAndroidService extends Service
{
private static native void sendToQt(String message);
private static final String TAG = "QtAndroidService";
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.i(TAG, "Creating Service");
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.i(TAG, "Destroying Service");
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
int ret = super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
String name = new String(intent.getByteArrayExtra("name"));
Log.i(TAG, "Service received name: " + name);
String message = "Hello " + name;
sendToQt(message);
Log.i(TAG, "Service sent back message: " + message);
return ret;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
}
In the overwritten method
onStartCommand()
, the service receives a name from the calling intent, then calls the native method
sendToQt(String message)
. For more information on managing native calls in Qt, see
Calling QML/C++ Functions from Java Code
.
To use the service, it must be declared in the
AndroidManifest.xml
file. When using pure Android Service in the main app process, use the following:
<service android:name=".QtAndroidService">
<!-- Background running -->
<meta-data android:name="android.app.background_running" android:value="true"/>
<!-- Background running -->
</service>
Before starting the service, register the native methods, then call the startService() method, as follows:
void QtAndroidService::sendToService(const QString &name) { QAndroidIntent serviceIntent(QtAndroid::androidActivity().object(), "org/qtproject/example/qtandroidservice/QtAndroidService"); serviceIntent.putExtra("name", name.toUtf8()); QAndroidJniObject result = QtAndroid::androidActivity().callObjectMethod( "startService", "(Landroid/content/Intent;)Landroid/content/ComponentName;", serviceIntent.handle().object()); }
This function is used to start the Service. If the service is already running, it will only send the names without starting a new service instance.
Then, you have to add the necessary Connections , as described in Qt JNI Messenger Example .
另请参阅 Android 服务 , Qt for Android ,和 Qt Android Extras .