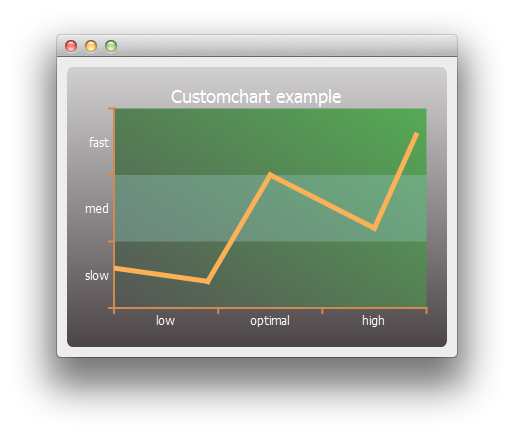
This example shows how to customize the appearance of the different elements on a chart.
要运行范例从 Qt Creator ,打开 欢迎 模式,然后选择范例从 范例 。更多信息,拜访 构建和运行范例 .
We begin by creating a simple line series and a chart object.
QLineSeries *series = new QLineSeries();
*series << QPointF(0, 6) << QPointF(9, 4) << QPointF(15, 20) << QPointF(25, 12) << QPointF(29, 26);
QChart *chart = new QChart();
chart->legend()->hide();
chart->addSeries(series);
First we customize the series and the chart's title and background.
// Customize series
QPen pen(QRgb(0xfdb157));
pen.setWidth(5);
series->setPen(pen);
// Customize chart title
QFont font;
font.setPixelSize(18);
chart->setTitleFont(font);
chart->setTitleBrush(QBrush(Qt::white));
chart->setTitle("Customchart example");
// Customize chart background
QLinearGradient backgroundGradient;
backgroundGradient.setStart(QPointF(0, 0));
backgroundGradient.setFinalStop(QPointF(0, 1));
backgroundGradient.setColorAt(0.0, QRgb(0xd2d0d1));
backgroundGradient.setColorAt(1.0, QRgb(0x4c4547));
backgroundGradient.setCoordinateMode(QGradient::ObjectBoundingMode);
chart->setBackgroundBrush(backgroundGradient);
// Customize plot area background
QLinearGradient plotAreaGradient;
plotAreaGradient.setStart(QPointF(0, 1));
plotAreaGradient.setFinalStop(QPointF(1, 0));
plotAreaGradient.setColorAt(0.0, QRgb(0x555555));
plotAreaGradient.setColorAt(1.0, QRgb(0x55aa55));
plotAreaGradient.setCoordinateMode(QGradient::ObjectBoundingMode);
chart->setPlotAreaBackgroundBrush(plotAreaGradient);
chart->setPlotAreaBackgroundVisible(true);
Then we customize the axes.
QCategoryAxis *axisX = new QCategoryAxis();
QCategoryAxis *axisY = new QCategoryAxis();
// Customize axis label font
QFont labelsFont;
labelsFont.setPixelSize(12);
axisX->setLabelsFont(labelsFont);
axisY->setLabelsFont(labelsFont);
// Customize axis colors
QPen axisPen(QRgb(0xd18952));
axisPen.setWidth(2);
axisX->setLinePen(axisPen);
axisY->setLinePen(axisPen);
// Customize axis label colors
QBrush axisBrush(Qt::white);
axisX->setLabelsBrush(axisBrush);
axisY->setLabelsBrush(axisBrush);
// Customize grid lines and shades
axisX->setGridLineVisible(false);
axisY->setGridLineVisible(false);
axisY->setShadesPen(Qt::NoPen);
axisY->setShadesBrush(QBrush(QColor(0x99, 0xcc, 0xcc, 0x55)));
axisY->setShadesVisible(true);
Then the axis label values and ranges. Once the axes are ready, we set them to be used by the chart.
axisX->append("low", 10);
axisX->append("optimal", 20);
axisX->append("high", 30);
axisX->setRange(0, 30);
axisY->append("slow", 10);
axisY->append("med", 20);
axisY->append("fast", 30);
axisY->setRange(0, 30);
chart->addAxis(axisX, Qt::AlignBottom);
chart->addAxis(axisY, Qt::AlignLeft);
series->attachAxis(axisX);
series->attachAxis(axisY);
Finally, we create a view containing the chart.
QChartView *chartView = new QChartView(chart);
chartView->setRenderHint(QPainter::Antialiasing);
Now we are ready to show the chart on a main window.
QMainWindow window;
window.setCentralWidget(chartView);
window.resize(400, 300);
window.show();