Example of a hybrid C++ and QML application demonstrating different axis formatters.
The Qt Quick axis formatter example shows how to use predefined axis formatters and how to create a custom one.
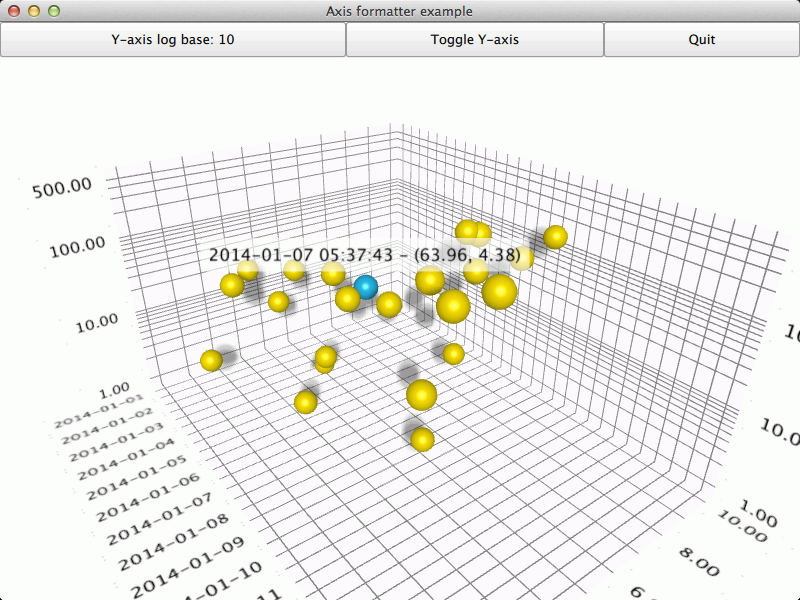
The interesting thing about this example is axis formatters, so we'll concentrate on that and skip explaining the basic functionality - for more detailed QML example documentation, see Qt Quick 2 Scatter Example .
要运行范例从 Qt Creator ,打开 欢迎 模式,然后选择范例从 范例 。更多信息,拜访 构建和运行范例 .
Customizing axis formatters requires subclassing the
QValue3DAxisFormatter
, which cannot be done in QML code alone. In this example we want an axis that interprets the float values as a timestamp and shows the date in the axis labels. To achieve this, we introduce a new class called
CustomFormatter
, which subclasses the
QValue3DAxisFormatter
:
class CustomFormatter : public QValue3DAxisFormatter { ...
Since float values of a QScatter3DSeries cannot be directly cast into QDateTime values due to difference in data width, we need some sort of mapping between the two. We chose to do the mapping by specifying an origin date for the formatter and interpreting the float values from the QScatter3DSeries as date offsets to that origin value. The origin date is given as a property:
Q_PROPERTY(QDate originDate READ originDate WRITE setOriginDate NOTIFY originDateChanged)
The mapping from value to
QDateTime
is done using
valueToDateTime()
方法:
QDateTime CustomFormatter::valueToDateTime(qreal value) const { return m_originDate.startOfDay().addMSecs(qint64(oneDayMs * value)); }
To function as an axis formatter, our
CustomFormatter
needs to reimplement some virtual methods:
virtual QValue3DAxisFormatter *createNewInstance() const; virtual void populateCopy(QValue3DAxisFormatter ©) const; virtual void recalculate(); virtual QString stringForValue(qreal value, const QString &format) const;
The first two are simple, we just create a new instance of
CustomFormatter
and copy the necessary data over to it. These two methods are used to create and update a cache of formatter for rendering purposes. It is important to remember to call the superclass implementation of
populateCopy()
:
QValue3DAxisFormatter *CustomFormatter::createNewInstance() const { return new CustomFormatter(); } void CustomFormatter::populateCopy(QValue3DAxisFormatter ©) const { QValue3DAxisFormatter::populateCopy(copy); CustomFormatter *customFormatter = static_cast<CustomFormatter *>(©); customFormatter->m_originDate = m_originDate; customFormatter->m_selectionFormat = m_selectionFormat; }
Bulk of the work done by
CustomFormatter
is done in the
recalculate()
method, where our formatter calculates the grid, subgrid, and label positions, as well as formats the label strings. In our custom formatter we ignore the segment count of the axis and draw a grid line always at midnight. Subsegment count and label positioning is handled normally:
void CustomFormatter::recalculate() { // We want our axis to always have gridlines at date breaks // Convert range into QDateTimes QDateTime minTime = valueToDateTime(qreal(axis()->min())); QDateTime maxTime = valueToDateTime(qreal(axis()->max())); // Find out the grid counts QTime midnight(0, 0); QDateTime minFullDate(minTime.date(), midnight); int gridCount = 0; if (minFullDate != minTime) minFullDate = minFullDate.addDays(1); QDateTime maxFullDate(maxTime.date(), midnight); gridCount += minFullDate.daysTo(maxFullDate) + 1; int subGridCount = axis()->subSegmentCount() - 1; // Reserve space for position arrays and label strings gridPositions().resize(gridCount); subGridPositions().resize((gridCount + 1) * subGridCount); labelPositions().resize(gridCount); labelStrings().reserve(gridCount); // Calculate positions and format labels qint64 startMs = minTime.toMSecsSinceEpoch(); qint64 endMs = maxTime.toMSecsSinceEpoch(); qreal dateNormalizer = endMs - startMs; qreal firstLineOffset = (minFullDate.toMSecsSinceEpoch() - startMs) / dateNormalizer; qreal segmentStep = oneDayMs / dateNormalizer; qreal subSegmentStep = 0; if (subGridCount > 0) subSegmentStep = segmentStep / qreal(subGridCount + 1); for (int i = 0; i < gridCount; i++) { qreal gridValue = firstLineOffset + (segmentStep * qreal(i)); gridPositions()[i] = float(gridValue); labelPositions()[i] = float(gridValue); labelStrings() << minFullDate.addDays(i).toString(axis()->labelFormat()); } for (int i = 0; i <= gridCount; i++) { if (subGridPositions().size()) { for (int j = 0; j < subGridCount; j++) { float position; if (i) position = gridPositions().at(i - 1) + subSegmentStep * (j + 1); else position = gridPositions().at(0) - segmentStep + subSegmentStep * (j + 1); if (position > 1.0f || position < 0.0f) position = gridPositions().at(0); subGridPositions()[i * subGridCount + j] = position; } } } }
The axis labels are formatted to show only the date, but for selection label we want little more resolution for the timestamp, so we specify another property for our custom formatter to allow user to customize it:
Q_PROPERTY(QString selectionFormat READ selectionFormat WRITE setSelectionFormat NOTIFY selectionFormatChanged)
This selection format property is used in the reimplemented
stringToValue
method, where we ignore the submitted format and substitute the custom selection format for it:
QString CustomFormatter::stringForValue(qreal value, const QString &format) const { Q_UNUSED(format) return valueToDateTime(value).toString(m_selectionFormat); }
To expose our new custom formatter to the QML, we must declare and register it:
Q_DECLARE_METATYPE(CustomFormatter *) ... qmlRegisterType<CustomFormatter>("CustomFormatter", 1, 0, "CustomFormatter");
In the QML codes, we define a different axis for each dimension:
axisZ: valueAxis axisY: logAxis axisX: dateAxis
Z-axis is just a regular ValueAxis3D :
ValueAxis3D { id: valueAxis segmentCount: 5 subSegmentCount: 2 labelFormat: "%.2f" min: 0 max: 10 }
For the Y-axis we define a logarithmic axis.
ValueAxis3D
can be made to show logarithmic scale by specifying
LogValueAxis3DFormatter
for
formatter
property of the axis:
ValueAxis3D { id: logAxis formatter: LogValueAxis3DFormatter { id: logAxisFormatter base: 10 autoSubGrid: true showEdgeLabels: true } labelFormat: "%.2f" }
And finally, for the X-axis we use our new
CustomFormatter
:
ValueAxis3D { id: dateAxis formatter: CustomFormatter { originDate: "2014-01-01" selectionFormat: "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" } subSegmentCount: 2 labelFormat: "yyyy-MM-dd" min: 0 max: 14 }
Rest of the application consists of fairly self-explanatory logic for modifying the axes and showing the graph.