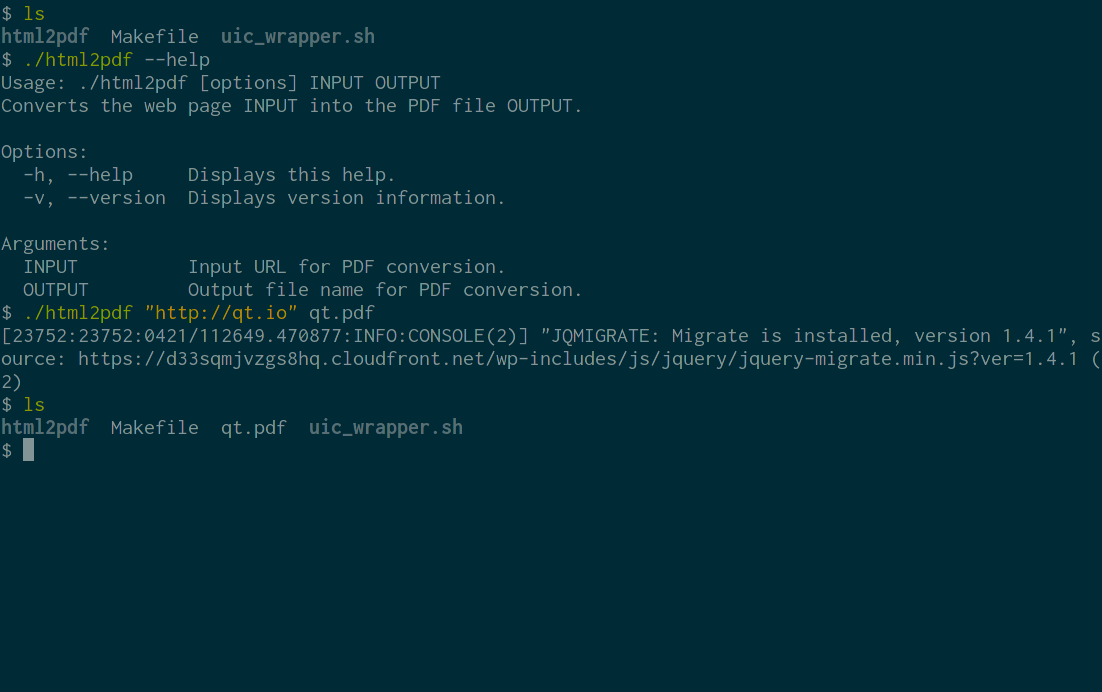
Html2Pdf demonstrates how to use Qt WebEngine to implement a command-line application for converting web pages into PDF documents.
要运行范例从 Qt Creator ,打开 欢迎 模式,然后选择范例从 范例 。更多信息,拜访 构建和运行范例 .
In order to convert a web page into a PDF document we need to:
This process is encapsulated in the Html2PdfConverter 类:
#include <QApplication> #include <QCommandLineParser> #include <QFile> #include <QTextStream> #include <QWebEnginePage> #include <functional> using namespace std; using namespace std::placeholders; class Html2PdfConverter : public QObject { Q_OBJECT public: explicit Html2PdfConverter(QString inputPath, QString outputPath); int run(); private slots: void loadFinished(bool ok); void pdfPrintingFinished(const QString &filePath, bool success); private: QString m_inputPath; QString m_outputPath; QScopedPointer<QWebEnginePage> m_page; };
In the constructor we create the QWebEnginePage and connect to its QWebEnginePage::loadFinished and QWebEnginePage::pdfPrintingFinished signals:
Html2PdfConverter::Html2PdfConverter(QString inputPath, QString outputPath) : m_inputPath(move(inputPath)) , m_outputPath(move(outputPath)) , m_page(new QWebEnginePage) { connect(m_page.data(), &QWebEnginePage::loadFinished, this, &Html2PdfConverter::loadFinished); connect(m_page.data(), &QWebEnginePage::pdfPrintingFinished, this, &Html2PdfConverter::pdfPrintingFinished); }
The
run()
method will trigger the conversion process by asking
QWebEnginePage
to start loading the target URL. We then enter the main event loop:
int Html2PdfConverter::run() { m_page->load(QUrl::fromUserInput(m_inputPath)); return QApplication::exec(); }
After the loading is finished we begin PDF generation. We ask the QWebEnginePage::printToPdf method to write the output directly to disk:
void Html2PdfConverter::loadFinished(bool ok) { if (!ok) { QTextStream(stderr) << tr("failed to load URL '%1'").arg(m_inputPath) << "\n"; QCoreApplication::exit(1); return; } m_page->printToPdf(m_outputPath); }
Once we receive the signal that the PDF conversion has finished, all that remains is to report potential errors and exit the program:
void Html2PdfConverter::pdfPrintingFinished(const QString &filePath, bool success) { if (!success) { QTextStream(stderr) << tr("failed to print to output file '%1'").arg(filePath) << "\n"; QCoreApplication::exit(1); } else { QCoreApplication::quit(); } }
Our
main
function is responsible for setting up a
QApplication
and parsing command line arguments:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { QApplication app(argc, argv); QCoreApplication::setOrganizationName("QtExamples"); QCoreApplication::setApplicationName("html2pdf"); QCoreApplication::setApplicationVersion(QT_VERSION_STR); QCommandLineParser parser; parser.setApplicationDescription( QCoreApplication::translate("main", "Converts the web page INPUT into the PDF file OUTPUT.")); parser.addHelpOption(); parser.addVersionOption(); parser.addPositionalArgument( QCoreApplication::translate("main", "INPUT"), QCoreApplication::translate("main", "Input URL for PDF conversion.")); parser.addPositionalArgument( QCoreApplication::translate("main", "OUTPUT"), QCoreApplication::translate("main", "Output file name for PDF conversion.")); parser.process(QCoreApplication::arguments()); const QStringList requiredArguments = parser.positionalArguments(); if (requiredArguments.size() != 2) parser.showHelp(1); Html2PdfConverter converter(requiredArguments.at(0), requiredArguments.at(1)); return converter.run(); }
Note that to use Qt WebEngine Widgets we need to create a QApplication and not a QCoreApplication , even though this is a command line application.