Just as widgets can contain other widgets, layouts can be used to provide different levels of grouping for widgets. Here, we want to display a label alongside a line edit at the top of a window, above a table view showing the results of a query.
We achieve this by creating two layouts:
queryLayout
是
QHBoxLayout
that contains
QLabel
and
QLineEdit
widgets placed side-by-side;
mainLayout
是
QVBoxLayout
that contains
queryLayout
和
QTableView
arranged vertically.
#include <QtWidgets> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { QApplication app(argc, argv); QWidget window; QLabel *queryLabel = new QLabel( QApplication::translate("nestedlayouts", "Query:")); QLineEdit *queryEdit = new QLineEdit(); QTableView *resultView = new QTableView(); QHBoxLayout *queryLayout = new QHBoxLayout(); queryLayout->addWidget(queryLabel); queryLayout->addWidget(queryEdit); QVBoxLayout *mainLayout = new QVBoxLayout(); mainLayout->addLayout(queryLayout); mainLayout->addWidget(resultView); window.setLayout(mainLayout); // Set up the model and configure the view... window.setWindowTitle( QApplication::translate("nestedlayouts", "Nested layouts")); window.show(); return app.exec(); } |
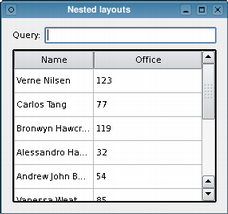
|
Note that we call the
mainLayout
's
addLayout()
function to insert the
queryLayout
above the
resultView
table.
We have omitted the code that sets up the model containing the data shown by the
QTableView
widget,
resultView
. For completeness, we show this below.
As well as QHBoxLayout and QVBoxLayout , Qt also provides QGridLayout and QFormLayout classes to help with more complex user interfaces. These can be seen if you run Qt Designer.
In the code above, we did not show where the table's data came from because we wanted to concentrate on the use of layouts. Here, we see that the model holds a number of items corresponding to rows, each of which is set up to contain data for two columns.
QStandardItemModel model;
model.setHorizontalHeaderLabels({ QApplication::translate("nestedlayouts", "Name"),
QApplication::translate("nestedlayouts", "Office") });
const QStringList rows[] = {
QStringList{ QStringLiteral("Verne Nilsen"), QStringLiteral("123") },
QStringList{ QStringLiteral("Carlos Tang"), QStringLiteral("77") },
QStringList{ QStringLiteral("Bronwyn Hawcroft"), QStringLiteral("119") },
QStringList{ QStringLiteral("Alessandro Hanssen"), QStringLiteral("32") },
QStringList{ QStringLiteral("Andrew John Bakken"), QStringLiteral("54") },
QStringList{ QStringLiteral("Vanessa Weatherley"), QStringLiteral("85") },
QStringList{ QStringLiteral("Rebecca Dickens"), QStringLiteral("17") },
QStringList{ QStringLiteral("David Bradley"), QStringLiteral("42") },
QStringList{ QStringLiteral("Knut Walters"), QStringLiteral("25") },
QStringList{ QStringLiteral("Andrea Jones"), QStringLiteral("34") }
};
QList<QStandardItem *> items;
for (const QStringList &row : rows) {
items.clear();
for (const QString &text : row)
items.append(new QStandardItem(text));
model.appendRow(items);
}
resultView->setModel(&model);
resultView->verticalHeader()->hide();
resultView->horizontalHeader()->setStretchLastSection(true);
The use of models and views is covered in the 项视图范例 and in the 模型/视图编程 概述。