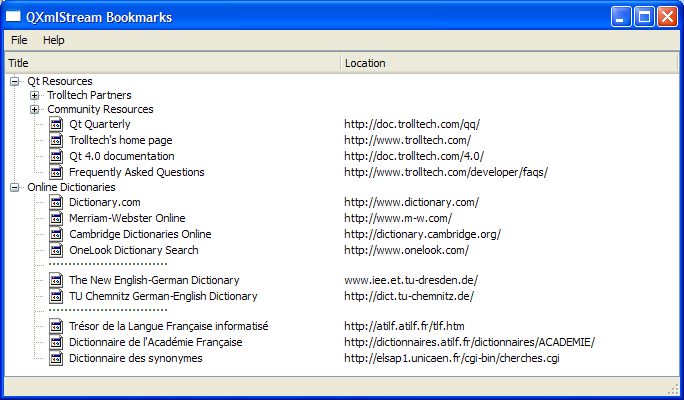
Demonstrates how to read and write to XBEL files.
The QXmlStream Bookmarks example provides a reader for XML Bookmark Exchange Language (XBEL) files using Qt's QXmlStreamReader class for reading, and QXmlStreamWriter class for writing the files.
The
XbelWriter
class contains a private instance of
QXmlStreamWriter
, which provides an XML writer with a streaming API.
XbelWriter
also has a reference to the
QTreeWidget
instance where the bookmark hierarchy is stored.
class XbelWriter { public: explicit XbelWriter(const QTreeWidget *treeWidget); bool writeFile(QIODevice *device); private: void writeItem(const QTreeWidgetItem *item); QXmlStreamWriter xml; const QTreeWidget *treeWidget; };
The
XbelWriter
constructor accepts a
treeWidget
to initialize within its definition. We enable
QXmlStreamWriter
's auto-formatting property to ensure line-breaks and indentations are added automatically to empty sections between elements, increasing readability as the data is split into several lines.
XbelWriter::XbelWriter(const QTreeWidget *treeWidget) : treeWidget(treeWidget) { xml.setAutoFormatting(true); }
The
writeFile()
function accepts a
QIODevice
object and sets it using
setDevice()
. This function then writes the document type definition(DTD), the start element, the version, and
treeWidget
's top-level items.
bool XbelWriter::writeFile(QIODevice *device) { xml.setDevice(device); xml.writeStartDocument(); xml.writeDTD(QStringLiteral("<!DOCTYPE xbel>")); xml.writeStartElement(QStringLiteral("xbel")); xml.writeAttribute(XbelReader::versionAttribute(), QStringLiteral("1.0")); for (int i = 0; i < treeWidget->topLevelItemCount(); ++i) writeItem(treeWidget->topLevelItem(i)); xml.writeEndDocument(); return true; }
The
writeItem()
function accepts a
QTreeWidgetItem
object and writes it to the stream, depending on its
tagName
, which can either be a "folder", "bookmark", or "separator".
void XbelWriter::writeItem(const QTreeWidgetItem *item) { QString tagName = item->data(0, Qt::UserRole).toString(); if (tagName == QLatin1String("folder")) { bool folded = !item->isExpanded(); xml.writeStartElement(tagName); xml.writeAttribute(XbelReader::foldedAttribute(), folded ? yesValue() : noValue()); xml.writeTextElement(titleElement(), item->text(0)); for (int i = 0; i < item->childCount(); ++i) writeItem(item->child(i)); xml.writeEndElement(); } else if (tagName == QLatin1String("bookmark")) { xml.writeStartElement(tagName); if (!item->text(1).isEmpty()) xml.writeAttribute(XbelReader::hrefAttribute(), item->text(1)); xml.writeTextElement(titleElement(), item->text(0)); xml.writeEndElement(); } else if (tagName == QLatin1String("separator")) { xml.writeEmptyElement(tagName); } }
The
XbelReader
contains a private instance of
QXmlStreamReader
, the companion class to
QXmlStreamWriter
.
XbelReader
also contains a reference to the
QTreeWidget
that is used to group the bookmarks according to their hierarchy.
class XbelReader { public: XbelReader(QTreeWidget *treeWidget); bool read(QIODevice *device); QString errorString() const; static inline QString versionAttribute() { return QStringLiteral("version"); } static inline QString hrefAttribute() { return QStringLiteral("href"); } static inline QString foldedAttribute() { return QStringLiteral("folded"); } private: void readXBEL(); void readTitle(QTreeWidgetItem *item); void readSeparator(QTreeWidgetItem *item); void readFolder(QTreeWidgetItem *item); void readBookmark(QTreeWidgetItem *item); QTreeWidgetItem *createChildItem(QTreeWidgetItem *item); QXmlStreamReader xml; QTreeWidget *treeWidget; QIcon folderIcon; QIcon bookmarkIcon; };
The
XbelReader
constructor accepts a
QTreeWidget
to initialize the
treeWidget
within its definition. A
QStyle
object is used to set
treeWidget
's style property. The
folderIcon
is set to QIcon::Normal mode where the pixmap is only displayed when the user is not interacting with the icon. The
QStyle::SP_DirClosedIcon
,
QStyle::SP_DirOpenIcon
,和
QStyle::SP_FileIcon
correspond to standard pixmaps that follow the style of your GUI.
XbelReader::XbelReader(QTreeWidget *treeWidget) : treeWidget(treeWidget) { QStyle *style = treeWidget->style(); folderIcon.addPixmap(style->standardPixmap(QStyle::SP_DirClosedIcon), QIcon::Normal, QIcon::Off); folderIcon.addPixmap(style->standardPixmap(QStyle::SP_DirOpenIcon), QIcon::Normal, QIcon::On); bookmarkIcon.addPixmap(style->standardPixmap(QStyle::SP_FileIcon)); }
The
read()
function accepts a
QIODevice
and sets it using
setDevice()
. The actual process of reading only takes place if the file is a valid XBEL 1.0 file. Note that the XML input needs to be well-formed to be accepted by
QXmlStreamReader
. Otherwise, the
raiseError()
function is used to display an error message. Since the XBEL reader is only concerned with reading XML elements, it makes extensive use of the
readNextStartElement()
convenience function.
bool XbelReader::read(QIODevice *device) { xml.setDevice(device); if (xml.readNextStartElement()) { if (xml.name() == QLatin1String("xbel") && xml.attributes().value(versionAttribute()) == QLatin1String("1.0")) { readXBEL(); } else { xml.raiseError(QObject::tr("The file is not an XBEL version 1.0 file.")); } } return !xml.error(); }
The
errorString()
function is used if an error occurred, in order to obtain a description of the error complete with line and column number information.
QString XbelReader::errorString() const { return QObject::tr("%1\nLine %2, column %3") .arg(xml.errorString()) .arg(xml.lineNumber()) .arg(xml.columnNumber()); }
The
readXBEL()
function reads the name of a startElement and calls the appropriate function to read it, depending on whether if its a "folder", "bookmark" or "separator". Otherwise, it calls
skipCurrentElement()
。
Q_ASSERT
() macro is used to provide a pre-condition for the function.
void XbelReader::readXBEL() { Q_ASSERT(xml.isStartElement() && xml.name() == QLatin1String("xbel")); while (xml.readNextStartElement()) { if (xml.name() == QLatin1String("folder")) readFolder(0); else if (xml.name() == QLatin1String("bookmark")) readBookmark(0); else if (xml.name() == QLatin1String("separator")) readSeparator(0); else xml.skipCurrentElement(); } }
The
readTitle()
function reads the bookmark's title.
void XbelReader::readTitle(QTreeWidgetItem *item) { Q_ASSERT(xml.isStartElement() && xml.name() == QLatin1String("title")); QString title = xml.readElementText(); item->setText(0, title); }
The
readSeparator()
function creates a separator and sets its flags. The text is set to 30 "0xB7", the HEX equivalent for period. The element is then skipped using
skipCurrentElement()
.
void XbelReader::readSeparator(QTreeWidgetItem *item) { Q_ASSERT(xml.isStartElement() && xml.name() == QLatin1String("separator")); QTreeWidgetItem *separator = createChildItem(item); separator->setFlags(item->flags() & ~Qt::ItemIsSelectable); separator->setText(0, QString(30, 0xB7)); xml.skipCurrentElement(); }
The
MainWindow
类是子类化的
QMainWindow
,采用
File
menu and a
帮助
菜单。
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow { Q_OBJECT public: MainWindow(); public slots: void open(); void saveAs(); void about(); #if !defined(QT_NO_CONTEXTMENU) && !defined(QT_NO_CLIPBOARD) void onCustomContextMenuRequested(const QPoint &pos); #endif private: void createMenus(); QTreeWidget *treeWidget; };
The
MainWindow
constructor instantiates the
QTreeWidget
对象,
treeWidget
and sets its header with a
QStringList
对象,
labels
. The constructor also invokes
createActions()
and
createMenus()
to set up the menus and their corresponding actions. The
statusBar()
is used to display the message "Ready" and the window's size is fixed to 480x320 pixels.
MainWindow::MainWindow() { QStringList labels; labels << tr("Title") << tr("Location"); treeWidget = new QTreeWidget; treeWidget->header()->setSectionResizeMode(QHeaderView::Stretch); treeWidget->setHeaderLabels(labels); #if !defined(QT_NO_CONTEXTMENU) && !defined(QT_NO_CLIPBOARD) treeWidget->setContextMenuPolicy(Qt::CustomContextMenu); connect(treeWidget, &QWidget::customContextMenuRequested, this, &MainWindow::onCustomContextMenuRequested); #endif setCentralWidget(treeWidget); createMenus(); statusBar()->showMessage(tr("Ready")); setWindowTitle(tr("QXmlStream Bookmarks")); const QSize availableSize = screen()->availableGeometry().size(); resize(availableSize.width() / 2, availableSize.height() / 3); }
The
open()
function enables the user to open an XBEL file using
QFileDialog::getOpenFileName
(). A warning message is displayed along with the
fileName
and
errorString
if the file cannot be read or if there is a parse error.
void MainWindow::open() { QString fileName = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, tr("Open Bookmark File"), QDir::currentPath(), tr("XBEL Files (*.xbel *.xml)")); if (fileName.isEmpty()) return; treeWidget->clear(); QFile file(fileName); if (!file.open(QFile::ReadOnly | QFile::Text)) { QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("QXmlStream Bookmarks"), tr("Cannot read file %1:\n%2.") .arg(QDir::toNativeSeparators(fileName), file.errorString())); return; } XbelReader reader(treeWidget); if (!reader.read(&file)) { QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("QXmlStream Bookmarks"), tr("Parse error in file %1:\n\n%2") .arg(QDir::toNativeSeparators(fileName), reader.errorString())); } else { statusBar()->showMessage(tr("File loaded"), 2000); } }
The
saveAs()
function displays a
QFileDialog
, prompting the user for a
fileName
使用
QFileDialog::getSaveFileName
(). Similar to the
open()
function, this function also displays a warning message if the file cannot be written to.
void MainWindow::saveAs() { QString fileName = QFileDialog::getSaveFileName(this, tr("Save Bookmark File"), QDir::currentPath(), tr("XBEL Files (*.xbel *.xml)")); if (fileName.isEmpty()) return; QFile file(fileName); if (!file.open(QFile::WriteOnly | QFile::Text)) { QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("QXmlStream Bookmarks"), tr("Cannot write file %1:\n%2.") .arg(QDir::toNativeSeparators(fileName), file.errorString())); return; } XbelWriter writer(treeWidget); if (writer.writeFile(&file)) statusBar()->showMessage(tr("File saved"), 2000); }
The
about()
function displays a
QMessageBox
with a brief description of the example.
void MainWindow::about() { QMessageBox::about(this, tr("About QXmlStream Bookmarks"), tr("The <b>QXmlStream Bookmarks</b> example demonstrates how to use Qt's " "QXmlStream classes to read and write XML documents.")); }
In order to implement the
open()
,
saveAs()
,
exit()
,
about()
and
aboutQt()
functions, we connect them to
QAction
objects and add them to the
fileMenu
and
helpMenu
. The connections are as shown below:
void MainWindow::createMenus() { QMenu *fileMenu = menuBar()->addMenu(tr("&File")); QAction *openAct = fileMenu->addAction(tr("&Open..."), this, &MainWindow::open); openAct->setShortcuts(QKeySequence::Open); QAction *saveAsAct = fileMenu->addAction(tr("&Save As..."), this, &MainWindow::saveAs); saveAsAct->setShortcuts(QKeySequence::SaveAs); QAction *exitAct = fileMenu->addAction(tr("E&xit"), this, &QWidget::close); exitAct->setShortcuts(QKeySequence::Quit); menuBar()->addSeparator(); QMenu *helpMenu = menuBar()->addMenu(tr("&Help")); helpMenu->addAction(tr("&About"), this, &MainWindow::about); helpMenu->addAction(tr("About &Qt"), qApp, &QCoreApplication::quit); }
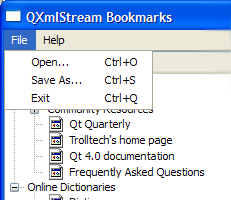
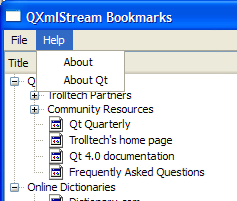
The
createMenus()
函数创建
fileMenu
and
helpMenu
and adds the
QAction
objects to them in order to create the menu shown in the screenshot below:
|
|
void MainWindow::createMenus() { QMenu *fileMenu = menuBar()->addMenu(tr("&File")); QAction *openAct = fileMenu->addAction(tr("&Open..."), this, &MainWindow::open); openAct->setShortcuts(QKeySequence::Open); QAction *saveAsAct = fileMenu->addAction(tr("&Save As..."), this, &MainWindow::saveAs); saveAsAct->setShortcuts(QKeySequence::SaveAs); QAction *exitAct = fileMenu->addAction(tr("E&xit"), this, &QWidget::close); exitAct->setShortcuts(QKeySequence::Quit); menuBar()->addSeparator(); QMenu *helpMenu = menuBar()->addMenu(tr("&Help")); helpMenu->addAction(tr("&About"), this, &MainWindow::about); helpMenu->addAction(tr("About &Qt"), qApp, &QCoreApplication::quit); }
main()
函数
The
main()
function instantiates
MainWindow
and invokes the
show()
函数。
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { QApplication app(argc, argv); MainWindow mainWin; mainWin.show(); mainWin.open(); return app.exec(); }
见 XML 书签交换语言资源页面 了解有关 XBEL 文件的更多信息。