The Bluetooth Picture Push example shows how to use the QBluetoothTransferManager API. The example transfers a local image to a remote device. Unfortunately this example cannot be used on Android as Qt does not support the Object Push Profile (OPP) on this platform.
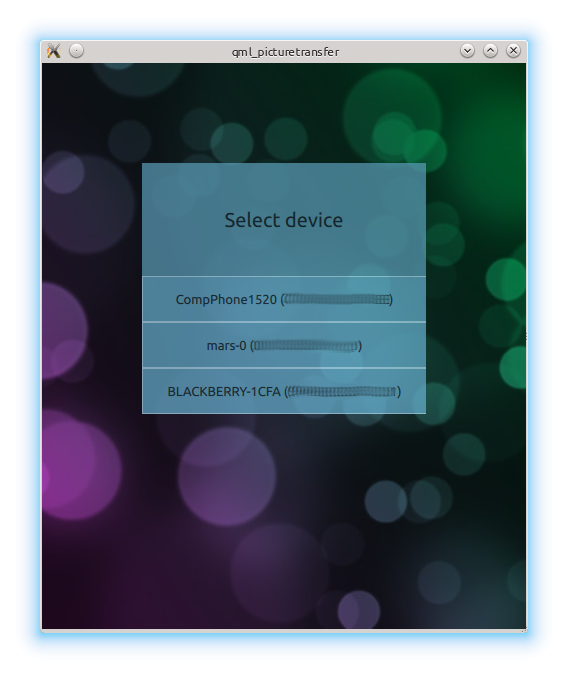
On the first user interface page the application scans for remote Bluetooth devices. The user must select the appropriate device to continue:
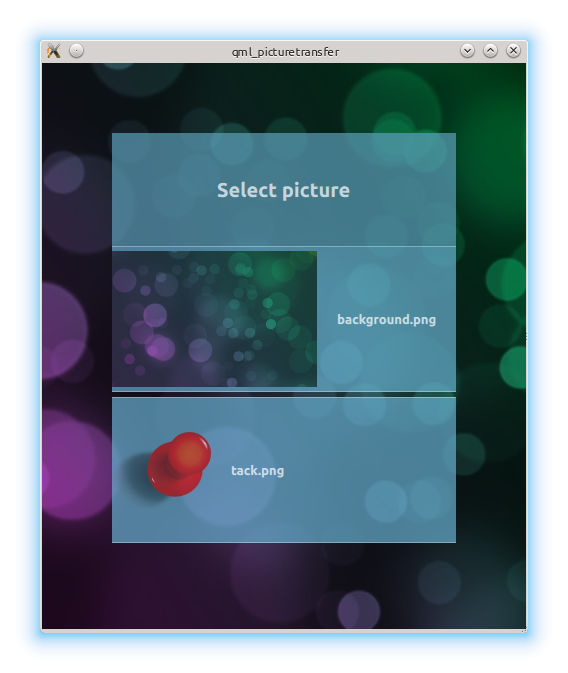
The next page presents a list of image files on the device. The files must be located under QStandardPaths::PicturesLocation }:
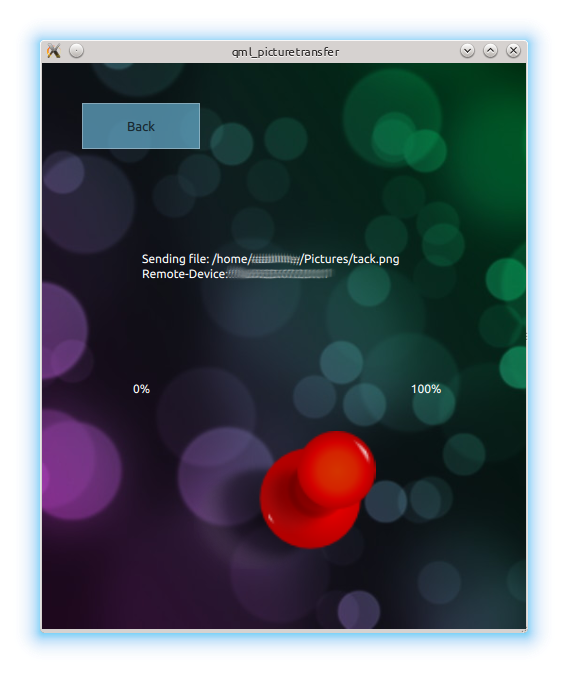
Once the picture was selected the UI shows the progress of the file transfer:
要运行范例从 Qt Creator ,打开 欢迎 模式,然后选择范例从 范例 。更多信息,拜访 构建和运行范例 .
The device discovery uses the
BluetoothDiscoveryModel
to detect the remote devices. Each discovery is displayed as an entry in a list. Once a device was selected the device address is stored in the
root
element. More details about the
root
element will follow further below.
ListView {
model: BluetoothDiscoveryModel {
discoveryMode: BluetoothDiscoveryModel.DeviceDiscovery
onErrorChanged: {
if (error == BluetoothDiscoveryModel.NoError)
return;
if (error == BluetoothDiscoveryModel.PoweredOffError)
titleLabel.text = "Bluetooth turned off";
else
titleLabel.text = "Cannot find devices";
}
}
delegate: Button {
width: listView.width + 2
text: model.name
onClicked: root.remoteDevice = model.remoteAddress
}
}
The file is selected with the help of
FolderListModel
. Once again the selected file is stored in the
root
元素:
model: FolderListModel {
folder: "file://"+SystemPictureFolder
showDirs: false
}
delegate: Rectangle {
Text {
text: model.fileName
}
MouseArea {
id: mArea
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: {
print ("path: " + model.filePath + " " + model.fileName)
root.fileName = model.filePath
}
}
}
The already mentioned
root
element collects the necessary pieces of data for the picture transfer. Once the file name has been set it triggers the file transfer:
Image { id: root property string remoteDevice; property string fileName; onFileNameChanged: { fileTransfer.initTransfer(remoteDevice, fileName); loader.source = "FileSending.qml" } onFileNameChanged: { fileTransfer.initTransfer(remoteDevice, fileName); loader.source = "FileSending.qml" }
The file transfer is implemented in C++:
void FileTransfer::initTransfer(QString address, QString fileName) { qDebug() << "Begin sharing file: " << address << fileName; QBluetoothAddress btAddress = QBluetoothAddress(address); QBluetoothTransferRequest request(btAddress); QFile *file = new QFile(fileName); reply = manager.put(request, file); connect(reply, SIGNAL(transferProgress(qint64,qint64)), this, SLOT(updateProgress(qint64,qint64))); }
and exposed to QML via a context property:
QQuickView view;
FileTransfer fileTransfer;
view.rootContext()->setContextProperty("fileTransfer", QVariant::fromValue(&fileTransfer));
文件:
另请参阅 Qt Bluetooth .