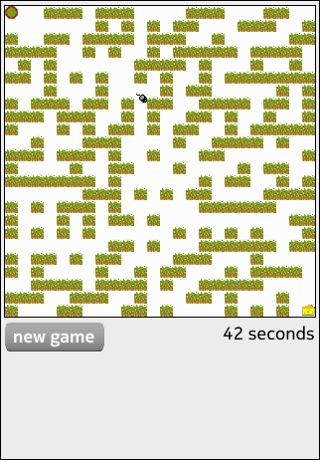
To write a QML application that will use the TiltSensor QML sensors type you need to do the following steps:
Import the QtSensors 5.x declarative plugin:
import QtSensors 5.0
Add the Sensor QML types into your qml file.
In this example we use the TiltSensor with values based in degrees and an accuracy of 5 degree:
TiltSensor {
id: tiltSensor
active: true
}
Starting the sensor can be done by setting the 'enabled' property to true:
onTriggered: {
if (!tiltSensor.enabled)
tiltSensor.active = true;
The mouse should move by a factor of the tilt value:
var xstep = 0;
xstep = tiltSensor.reading.yRotation * 0.1 //acceleration
var ystep = 0;
ystep = tiltSensor.reading.xRotation * 0.1 //acceleration
The walk direction of the mouse takes into account some collision detection:
if (xstep < 1 && xstep > 0)
xstep = 0
else if (xstep > -1 && xstep < 0)
xstep = 0
if (ystep < 1 && ystep > 0)
ystep = 0;
else if (ystep > -1 && ystep < 0)
ystep = 0;
if ((xstep < 0 && mouseCtrl.x > 0
&& Lib.canMove(mouseCtrl.x + xstep,mouseCtrl.y))) {
xval = mouseCtrl.x + xstep;
} else if (xstep > 0 && mouseCtrl.x < (Lib.cellDimension * (Lib.dimension - 1))
&& Lib.canMove(mouseCtrl.x + xstep,mouseCtrl.y)) {
xval = mouseCtrl.x + xstep;
} else
xval = mouseCtrl.x;
if (ystep < 0 && mouseCtrl.y > 0
&& Lib.canMove(mouseCtrl.x, mouseCtrl.y + ystep)) {
yval = mouseCtrl.y + ystep;
} else if (ystep > 0 && (mouseCtrl.y < (Lib.cellDimension * (Lib.dimension - 1)))
&& Lib.canMove(mouseCtrl.x, mouseCtrl.y + ystep)) {
yval = mouseCtrl.y + ystep;
} else
yval = mouseCtrl.y
mouseCtrl.move(xval, yval);
The rotation of the mouse image is determined according to the angle that the mouse is moving.
var a = newy - mouse.y
var b = newx - mouse.x
var radians_to_degrees = 57.2957795
angle = Math.atan2(-b, a) * radians_to_degrees
if (angle < 0)
angle = 360 + angle
img.rotation = angle
mouse.x = newx;
mouse.y = newy;
文件: