Defines an arc with the given radius. 更多...
| import 语句: | import QtQuick 2.12 |
PathArc provides a simple way of specifying an arc that ends at a given position and uses the specified radius. It is modeled after the SVG elliptical arc command.
The following QML produces the path shown below:

|
Path { startX: 100; startY: 0 PathArc { x: 0; y: 100 radiusX: 100; radiusY: 100 useLargeArc: true } } |
Note that a single PathArc cannot be used to specify a circle. Instead, you can use two PathArc elements, each specifying half of the circle.
另请参阅 Path , PathLine , PathQuad , PathCubic , PathAngleArc , PathCurve ,和 PathSvg .
|
direction : enumeration |
Defines the direction of the arc. Possible values are PathArc .Clockwise (default) and PathArc .Counterclockwise.
The following QML can produce either of the two illustrated arcs below by changing the value of direction.

|
Path { startX: 50; startY: 50 PathArc { x: 150; y: 50 radiusX: 75; radiusY: 50 } } |
另请参阅 useLargeArc .
|
radiusX : real |
Defines the radius of the arc.
The following QML demonstrates how different radius values can be used to change the shape of the arc:

|
Path { startX: 0; startY: 100 PathArc { relativeX: 50; y: 100 radiusX: 25; radiusY: 15 } PathArc { relativeX: 50; y: 100 radiusX: 25; radiusY: 25 } PathArc { relativeX: 50; y: 100 radiusX: 25; radiusY: 50 } PathArc { relativeX: 50; y: 100 radiusX: 50; radiusY: 100 } } |
|
radiusY : real |
Defines the radius of the arc.
The following QML demonstrates how different radius values can be used to change the shape of the arc:

|
Path { startX: 0; startY: 100 PathArc { relativeX: 50; y: 100 radiusX: 25; radiusY: 15 } PathArc { relativeX: 50; y: 100 radiusX: 25; radiusY: 25 } PathArc { relativeX: 50; y: 100 radiusX: 25; radiusY: 50 } PathArc { relativeX: 50; y: 100 radiusX: 50; radiusY: 100 } } |
|
relativeX : real |
Defines the end point of the arc relative to its start.
If both a relative and absolute end position are specified for a single axis, the relative position will be used.
Relative and absolute positions can be mixed, for example it is valid to set a relative x and an absolute y.
|
relativeY : real |
Defines the end point of the arc relative to its start.
If both a relative and absolute end position are specified for a single axis, the relative position will be used.
Relative and absolute positions can be mixed, for example it is valid to set a relative x and an absolute y.
|
useLargeArc : bool |
Whether to use a large arc as defined by the arc points.
Given fixed start and end positions, radius, and direction, there are two possible arcs that can fit the data. useLargeArc is used to distinguish between these. For example, the following QML can produce either of the two illustrated arcs below by changing the value of useLargeArc.

|
Path { startX: 0; startY: 100 PathArc { x: 100; y: 200 radiusX: 100; radiusY: 100 direction: PathArc.Clockwise } } |
默认值为 false。
|
x : real |
Defines the end point of the arc.
另请参阅 relativeX and relativeY .
|
xAxisRotation : real |
Defines the rotation of the arc, in degrees. The default value is 0.
An arc is a section of circles or ellipses. Given the radius and the start and end points, there are two ellipses that connect the points. This property defines the rotation of the X axis of these ellipses.
注意: The value is only useful when the x and y radius differ, meaning the arc is a section of ellipses.
The following QML demonstrates how different radius values can be used to change the shape of the arc:
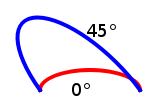
|
Path { startX: 50; startY: 100 PathArc { x: 150; y: 100 radiusX: 50; radiusY: 20 xAxisRotation: 45 } } |
|
y : real |
Defines the end point of the arc.