Demonstrates using Qt Quick item as a texture with three.js.
This example demonstrates how to implement an application that uses Qt Quick 2D element as a texture in a three.js scene. The example shows a 3D model of a mobile phone with an UI implemented with Qt Quick. When the phone is not rotating, the UI can be interacted with.
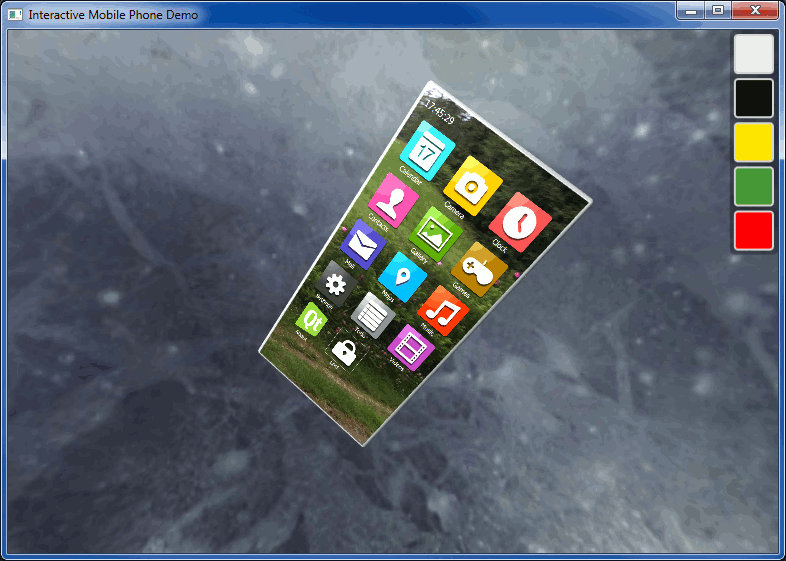
The Qt Quick Implementation
main.qml
of the example renders the 3D model of the mobile phone using Canvas3D type. The phone UI is composed of the
textureSource
Qt Quick item and its children. To make it possible to use the item as a texture source for Canvas3D, we must enable the layer of the item:
Item { id: textureSource layer.enabled: true layer.smooth: true layer.textureMirroring: ShaderEffectSource.NoMirroring ...
The texture mirroring is disabled so that the OpenGL texture generated from the item is oriented as the three.js expects.
The
textureSource
item is passed as a parameter to the JavaScript function handling the OpenGL initialization in Canvas3D:
onInitializeGL: GLCode.initializeGL(canvas3d, textureSource)
The texture generated from the
textureSource
is not interactable by itself, as it is just a regular texture. To make it appear interactable, we make it so that the phone UI is interactable only when the phone is not rotating and superimpose the actual
textureSource
item over the Canvas3D so that both the 3D model and the
textureSource
items are perfectly aligned. The 3D model and the Qt Quick UI are aligned by careful positioning of the model and scaling of the
textureSource
item using its
transform
property. The
textureSource
item is set fully transparent so that there are no visual artifacts:
transform: [ Scale { origin.y: textureSource.height / 2 origin.x: textureSource.width / 2 yScale: 0.5 * mainView.height / mainView.initialHeight xScale: 0.5 * mainView.height / mainView.initialHeight } ] opacity: 0.0
To ensure user cannot interact with the UI when the phone is rotating, we hide the
textureSource
item behind the Canvas3D by adjusting its
z
property when the phone starts its rotation animation.
The JavaScript side of the implementation,
cellphone.js
, is done using a version of
three.js
that is ported for
Qt Canvas 3D
:
three.js
.
The
initializeGL()
method creates the scene. It also adds the lights and the camera to the scene and creates materials and meshes used in the scene. The part relevant to the main point of this example is how the
textureSource
is handled. It is very simple to create a texture from a Qt Quick texture source: simply create a new
THREE.QtQuickItemTexture
采用
textureSource
as a parameter and you are done:
var frontTexture = new THREE.QtQuickItemTexture( textureSource );
The texture created this way can be used as a map to a material just like a regular texture:
var frontMaterial = new THREE.MeshPhongMaterial( { map: frontTexture } );
The scene is rendered in
paintGL()
method, which simply adjusts the rotations of the phone meshes, repositions the camera and light, and renders the scene.
For more information on how to use
three.js
the documentation is available here:
three.js/docs
The background sphere uses Pluto texture map, which is Copyright (c) by James Hastings-Trew http://planetpixelemporium.com/planets.html . Used with permission.
文件:
图像: