Renders a path. 更多...
| import 语句: | import QtQuick.Shapes 1.15 |
| Since: | Qt 5.10 |
| 继承: | |
| 继承者: |
Renders a path either by generating geometry via
QPainterPath
and manual triangulation or by using a GPU vendor extension like
GL_NV_path_rendering
.
This approach is different from rendering shapes via QQuickPaintedItem or the 2D Canvas because the path never gets rasterized in software. Therefore Shape is suitable for creating shapes spreading over larger areas of the screen, avoiding the performance penalty for texture uploads or framebuffer blits. In addition, the declarative API allows manipulating, binding to, and even animating the path element properties like starting and ending position, the control points, and so on.
The types for specifying path elements are shared between PathView and Shape. However, not all Shape implementations support all path element types, while some may not make sense for PathView . Shape's currently supported subset is: PathMove , PathLine , PathQuad , PathCubic , PathArc ,和 PathSvg .
见 Path for a detailed overview of the supported path elements.
Shape { width: 200 height: 150 anchors.centerIn: parent ShapePath { strokeWidth: 4 strokeColor: "red" fillGradient: LinearGradient { x1: 20; y1: 20 x2: 180; y2: 130 GradientStop { position: 0; color: "blue" } GradientStop { position: 0.2; color: "green" } GradientStop { position: 0.4; color: "red" } GradientStop { position: 0.6; color: "yellow" } GradientStop { position: 1; color: "cyan" } } strokeStyle: ShapePath.DashLine dashPattern: [ 1, 4 ] startX: 20; startY: 20 PathLine { x: 180; y: 130 } PathLine { x: 20; y: 130 } PathLine { x: 20; y: 20 } } }
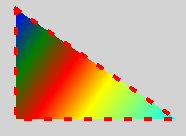
像 Item , Shape also allows any visual or non-visual objects to be declared as children. ShapePath objects are handled specially. This is useful since it allows adding visual items, like Rectangle or Image , and non-visual objects, like Timer directly as children of Shape.
The following list summarizes the available Shape rendering approaches:
GL_NV_path_rendering
methods are available. By default only the generic approach is used. Setting Shape.vendorExtensionsEnabled property to
true
leads to using NV_path_rendering on NVIDIA systems when running directly on OpenGL, and the generic method on others. When OpenGL is not used directly by the scene graph, for example because it is using the graphics abstraction layer (QRhi), only the generic shape renderer is available.
software
backend is fully supported. The path is rendered via
QPainter::strokePath()
and
QPainter::fillPath()
在此情况下。
When using Shape, it is important to be aware of potential performance implications:
GL_NV_path_rendering
where the cost of property changes is smaller.
GL_NV_path_rendering
. The way such a Shape item is represented in the scene graph is different from an ordinary geometry-based item, and incurs a certain cost when it comes to OpenGL state changes.
另请参阅 Qt Quick 范例 - 形状 , Path , PathMove , PathLine , PathQuad , PathCubic , PathArc ,和 PathSvg .
|
asynchronous : bool |
当
rendererType
is
Shape.GeometryRenderer
, the input path is triangulated on the CPU during the polishing phase of the Shape. This is potentially expensive. To offload this work to separate worker threads, set this property to
true
.
When enabled, making a Shape visible will not wait for the content to become available. Instead, the GUI/main thread is not blocked and the results of the path rendering are shown only when all the asynchronous work has been finished.
默认值为
false
.
|
containsMode : enumeration |
This property determines the definition of contains() for the Shape. It is useful in case you add Qt Quick 输入处理程序 and you want to react only when the mouse or touchpoint is fully inside the Shape.
| 常量 | 描述 |
|---|---|
Shape.BoundingRectContains
|
默认实现的 QQuickItem::contains() checks only whether the given point is inside the rectangular bounding box. This is the most efficient implementation, which is why it's the default. |
Shape.FillContains
|
Check whether the interior (the part that would be filled if you are rendering it with fill) of any ShapePath that makes up this Shape contains the given point. The more complex and numerous ShapePaths you add, the less efficient this is to check, which can potentially slow down event delivery in your application. So it should be used with care. |
One way to speed up the
FillContains
check is to generate an approximate outline with as few points as possible, place that in a transparent Shape on top, and add your Pointer Handlers to that, so that the containment check is cheaper during event delivery.
This property was introduced in QtQuick.Shapes 1.11.
|
[default] data : list < 对象 > |
此特性保持 ShapePath objects that define the contents of the Shape. It can also contain any other type of objects, since Shape, like Item, allows adding any visual or non-visual objects as children.
|
[read-only] rendererType : enumeration |
This property determines which path rendering backend is active.
| 常量 | 描述 |
|---|---|
Shape.UnknownRenderer
|
The renderer is unknown. |
Shape.GeometryRenderer
|
The generic, driver independent solution for OpenGL. Uses the same CPU-based triangulation approach as QPainter 's OpenGL 2 paint engine. This is the default on non-NVIDIA hardware when the default, OpenGL Qt Quick scenegraph backend is in use. |
Shape.NvprRenderer
|
Path items are rendered by performing OpenGL calls using the
GL_NV_path_rendering
extension. This is the default on NVIDIA hardware when the default, OpenGL Qt Quick scenegraph backend is in use.
|
Shape.SoftwareRenderer
|
Pure
QPainter
drawing using the raster paint engine. This is the default, and only, option when the Qt Quick scenegraph is running with the
software
backend.
|
|
[read-only] status : enumeration |
This property determines the status of the Shape and is relevant when Shape.asynchronous is set to
true
.
| 常量 | 描述 |
|---|---|
Shape.Null
|
Not yet initialized. |
Shape.Ready
|
The Shape has finished processing. |
Shape.Processing
|
The path is being processed. |