The QScrollBar 小部件提供垂直 (或水平) 滚动条。 更多...
| 头: | #include <QScrollBar> |
| qmake: | QT += widgets |
| 继承: | QAbstractSlider |
| QScrollBar (QWidget * parent = Q_NULLPTR) | |
| QScrollBar (Qt::Orientation orientation , QWidget * parent = Q_NULLPTR) | |
| ~QScrollBar () |
| virtual bool | event (QEvent * event ) |
| virtual QSize | sizeHint () const |
| void | initStyleOption (QStyleOptionSlider * option ) const |
| virtual void | contextMenuEvent (QContextMenuEvent * event ) |
| virtual void | hideEvent ( QHideEvent * ) |
| virtual void | mouseMoveEvent (QMouseEvent * e ) |
| virtual void | mousePressEvent (QMouseEvent * e ) |
| virtual void | mouseReleaseEvent (QMouseEvent * e ) |
| virtual void | paintEvent ( QPaintEvent * ) |
| virtual void | sliderChange (SliderChange change ) |
| virtual void | wheelEvent (QWheelEvent * event ) |
The QScrollBar 小部件提供垂直 (或水平) 滚动条。
滚动条是控件,使用户能够访问 > 用于显示文档的 Widget 的文档部分。它为用户提供当前文档位置及可见文档数量的视觉指示。滚动条通常装备有其它控件,使导航更精确。Qt 以适合各平台的方式显示滚动条。
If you need to provide a scrolling view onto another widget, it may be more convenient to use the QScrollArea class because this provides a viewport widget and scroll bars. QScrollBar is useful if you need to implement similar functionality for specialized widgets using QAbstractScrollArea ; for example, if you decide to subclass QAbstractItemView . For most other situations where a slider control is used to obtain a value within a given range, the QSlider class may be more appropriate for your needs.
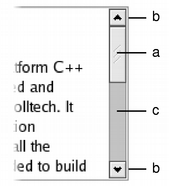
|
Scroll bars typically include four separate controls: a slider, scroll arrows, and a page control.
|
Each scroll bar has a value that indicates how far the slider is from the start of the scroll bar; this is obtained with value () 和设置采用 setValue (). This value always lies within the range of values defined for the scroll bar, from minimum() to maximum() inclusive. The range of acceptable values can be set with setMinimum () 和 setMaximum (). At the minimum value, the top edge of the slider (for a vertical scroll bar) or left edge (for a horizontal scroll bar) will be at the top (or left) end of the scroll bar. At the maximum value, the bottom (or right) edge of the slider will be at the bottom (or right) end of the scroll bar.
The length of the slider is usually related to the value of the page step, and typically represents the proportion of the document area shown in a scrolling view. The page step is the amount that the value changes by when the user presses the Page Up and Page Down keys, and is set with setPageStep (). Smaller changes to the value defined by the line step are made using the cursor keys, and this quantity is set with setSingleStep() .
Note that the range of values used is independent of the actual size of the scroll bar widget. You do not need to take this into account when you choose values for the range and the page step.
The range of values specified for the scroll bar are often determined differently to those for a QSlider because the length of the slider needs to be taken into account. If we have a document with 100 lines, and we can only show 20 lines in a widget, we may wish to construct a scroll bar with a page step of 20, a minimum value of 0, and a maximum value of 80. This would give us a scroll bar with five "pages".
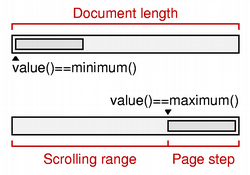
|
The relationship between a document length, the range of values used in a scroll bar, and the page step is simple in many common situations. The scroll bar's range of values is determined by subtracting a chosen page step from some value representing the length of the document. In such cases, the following equation is useful: document length = maximum () - minimum () + pageStep (). |
QScrollBar 仅提供整数范围。注意,尽管 QScrollBar handles very large numbers, scroll bars on current screens cannot usefully represent ranges above about 100,000 pixels. Beyond that, it becomes difficult for the user to control the slider using either the keyboard or the mouse, and the scroll arrows will have limited use.
ScrollBar inherits a comprehensive set of signals from QAbstractSlider :
A scroll bar can be controlled by the keyboard, but it has a default focusPolicy () of Qt::NoFocus 。使用 setFocusPolicy () to enable keyboard interaction with the scroll bar:
The slider itself can be controlled by using the triggerAction() function to simulate user interaction with the scroll bar controls. This is useful if you have many different widgets that use a common range of values.
大多数 GUI 样式使用 pageStep () value to calculate the size of the slider.
另请参阅 QScrollArea , QSlider , QDial , QSpinBox , GUI Design Handbook: Scroll Bar ,和 滑块范例 .
构造垂直滚动条。
The parent 自变量被发送给 QWidget 构造函数。
The minimum 默认为 0, maximum 到 99,采用 singleStep 1 尺寸和 pageStep 10 尺寸,及初始 value of 0.
构造滚动条采用给定 orientation .
The parent 自变量会被传递给 QWidget 构造函数。
The minimum 默认为 0, maximum 到 99,采用 singleStep 1 尺寸和 pageStep 10 尺寸,及初始 value of 0.
销毁滚动条。
[virtual protected]
void
QScrollBar::
contextMenuEvent
(
QContextMenuEvent
*
event
)
重实现自 QWidget::contextMenuEvent ().
[虚拟]
bool
QScrollBar::
event
(
QEvent
*
event
)
重实现自 QObject::event ().
[virtual protected]
void
QScrollBar::
hideEvent
(
QHideEvent *
)
重实现自 QWidget::hideEvent ().
[protected]
void
QScrollBar::
initStyleOption
(
QStyleOptionSlider
*
option
) const
初始化 option 采用值来自此 QScrollBar 。此方法对子类是有用的,当需要 QStyleOptionSlider ,但不希望自己填充所有信息。
另请参阅 QStyleOption::initFrom ().
[virtual protected]
void
QScrollBar::
mouseMoveEvent
(
QMouseEvent
*
e
)
重实现自 QWidget::mouseMoveEvent ().
[virtual protected]
void
QScrollBar::
mousePressEvent
(
QMouseEvent
*
e
)
重实现自 QWidget::mousePressEvent ().
[virtual protected]
void
QScrollBar::
mouseReleaseEvent
(
QMouseEvent
*
e
)
重实现自 QWidget::mouseReleaseEvent ().
[virtual protected]
void
QScrollBar::
paintEvent
(
QPaintEvent *
)
重实现自 QWidget::paintEvent ().
[虚拟]
QSize
QScrollBar::
sizeHint
() const
重实现自 QWidget::sizeHint ().
[virtual protected]
void
QScrollBar::
sliderChange
(
SliderChange
change
)
重实现自 QAbstractSlider::sliderChange ().
[virtual protected]
void
QScrollBar::
wheelEvent
(
QWheelEvent
*
event
)
重实现自 QWidget::wheelEvent ().