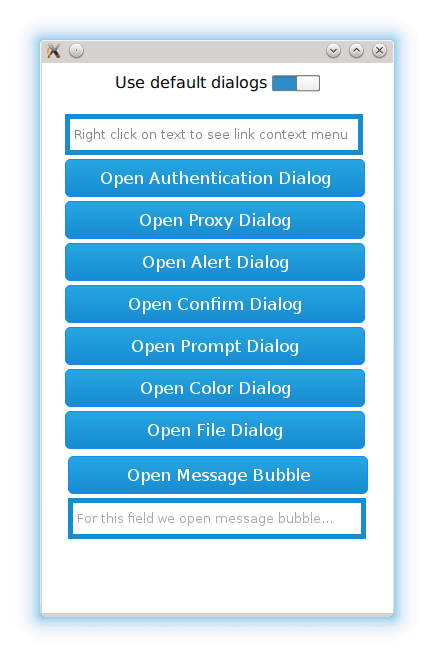
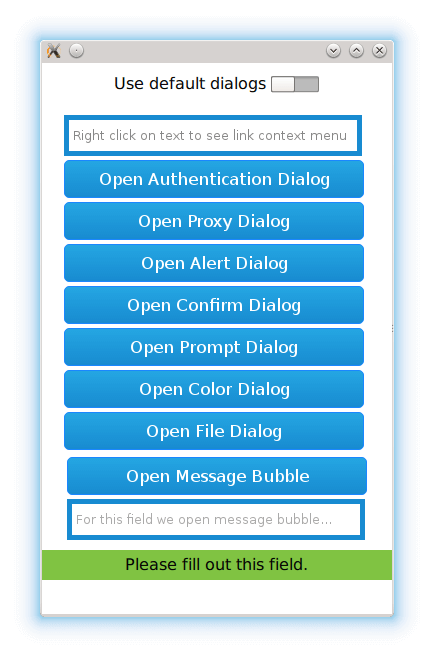
A web page might request dialogs for various purposes, such as authentication, picking colors, choosing files, and responding to JavaScript alerts, confirmation requests, and prompts.
自定义对话框 demonstrates how to use WebEngine dialog request objects to implement custom dialogs for use instead of the default dialogs.
要运行范例从 Qt Creator ,打开 欢迎 模式,然后选择范例从 范例 。更多信息,拜访 构建和运行范例 .
In this example, we create a simple
index.html
page that contains buttons and text fields for triggering a context menu and the following dialogs:
As mentioned, the index.html file is responsible for triggering the dialogs from the side of HTML and JavaScript. Additionally, the example program starts a localhost TCP server returning the mocked HTTP responses needed to trigger proxy and HTTP authentication dialogs.
The custom dialogs are just Qt Quick Designer UI Forms without any business logic. The point here is to present the glue code that is required to display the custom dialog for a particular web engine dialog or a menu request.
在
main.cpp
, we initialize the WebEngine the same way as in the
WebEngine Qt Quick 最小范例
:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { Application app(argc, argv); QtWebEngine::initialize(); QQmlApplicationEngine engine; Server *server = new Server(&engine); engine.load(QUrl(QStringLiteral("qrc:/main.qml"))); QTimer::singleShot(0, server, &Server::run); QNetworkProxy proxy; proxy.setType(QNetworkProxy::HttpProxy); proxy.setHostName("localhost"); proxy.setPort(5555); QNetworkProxy::setApplicationProxy(proxy); return app.exec(); }
In addition, we set up a proxy and a TCP server to be able to simulate proxy and HTTP authetication requests.
在
main.qml
, we create a top level window, which contains a
StackView
with a SwitchButton and a
WebView
:
import QtQuick.Window 2.0 Window { width: 350 height: 550 visible: true Controls.StackView { id: stackView anchors.fill: parent focus: true initialItem: Item { id: main width: parent.width height: parent.height ColumnLayout { anchors.fill: parent SwitchButton { id: switcher Layout.fillWidth: true } WebView { id: webView useDefaultDialogs: switcher.checked Layout.fillWidth: true Layout.fillHeight: true } } } function closeForm() { pop(main); } function openForm(form) { push(form); currentItem.closeForm.connect(closeForm); } } Component.onCompleted: { webView.openForm.connect(stackView.openForm); } }
In this example, we implement the handling of the following web engine requests:
ContextMenuRequest
is a request object that is passed as a parameter of the
WebEngineView::contextMenuRequested
signal. We use the
onContextMenuRequested
signal handler to handle requests for
#openMenu
URL links:
WebEngineView { ... onContextMenuRequested: function(request) { // we only show menu for links with #openMenu if (!request.linkUrl.toString().endsWith("#openMenu")) { request.accepted = true; return; } // return early to show default menu if (useDefaultDialogs) return; request.accepted = true; openForm({item: Qt.resolvedUrl("forms/Menu.qml"), properties: {"request": request}}); } ... }
The first text field from the top on our page triggers the request. Next, we check whether we should use the default menu. If not, we accept the request and switch the view to show the
MenuForm
:

MenuForm { property QtObject request signal closeForm() followLink.onClicked: closeForm() back.onClicked: closeForm() forward.onClicked: closeForm() reload.onClicked: closeForm() copyLinkUrl.onClicked: closeForm() saveLink.onClicked: closeForm() close.onClicked: closeForm() Component.onCompleted: { back.btnEnable = false; forward.btnEnable = false; } }
To keep things simple, we do not provide any logic on component completion, and we simply close the form on any action.
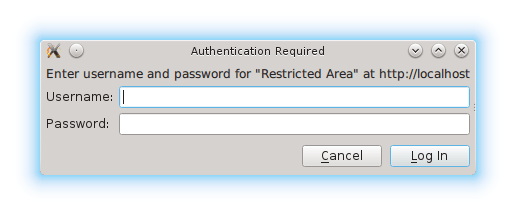
AuthenticationDialogRequest is a request object that is passed as a parameter of the WebEngineView::authenticationDialogRequested signal:
WebEngineView { ... onAuthenticationDialogRequested: function(request) { if (useDefaultDialogs) return; request.accepted = true; openForm({item: Qt.resolvedUrl("forms/Authentication.qml"), properties: {"request": request}}); } ... }
使用
onAuthenticationDialogRequested
signal handler to check whether we should use the default authentication dialog. If not, we accept the request and switch the view to show the
AuthenticationForm
:
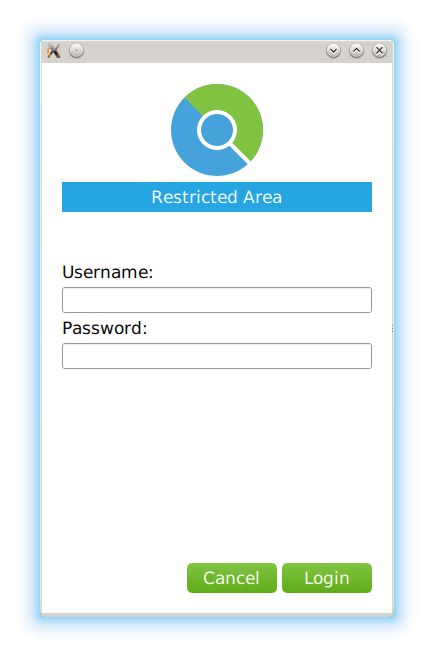
AuthenticationForm { property QtObject request signal closeForm() cancelButton.onClicked: { request.dialogReject(); closeForm(); } loginButton.onClicked: { request.dialogReject(); closeForm(); } Component.onCompleted: { switch (request.type) { case AuthenticationDialogRequest.AuthenticationTypeHTTP: console.log("HTTP Authentication Required. Host says: " + request.realm); break; case AuthenticationDialogRequest.AuthenticationTypeProxy: console.log("Proxy Authentication Required for: " + request.proxyHost); break; } } }
On component completion, we log the request type. The user can fill in the credentials and click
Login
. We provide
onClicked
handlers to accept or reject the authentication dialog. The TCP server on localhost does not handle real authentication, and therefore we call
rejectDialog()
而不是
acceptDialog()
also for the login button
clicked
信号。
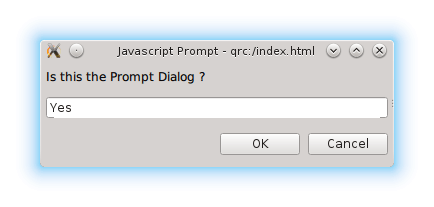
JavaScriptDialogRequest is a request object that is passed as a parameter of the WebEngineView::javaScriptDialogRequested signal:
WebEngineView { ... onJavaScriptDialogRequested: function(request) { if (useDefaultDialogs) return; request.accepted = true; openForm({item: Qt.resolvedUrl("forms/JavaScript.qml"), properties: {"request": request}}); } ... }
使用
onJavaScriptDialogRequested
signal handler to check whether we should use the default JavaScript dialog. If not, we accept the request and switch the view to show the
JavaScriptForm
:

JavaScriptForm { property QtObject request signal closeForm() cancelButton.onClicked: { request.dialogReject(); closeForm(); } okButton.onClicked: { request.dialogAccept(prompt.text); closeForm(); } Component.onCompleted: { switch (request.type) { case JavaScriptDialogRequest.DialogTypeAlert: cancelButton.visible = false; title = qsTr("Alert"); message = request.message; prompt.text = ""; prompt.visible = false; break; case JavaScriptDialogRequest.DialogTypeConfirm: title = qsTr("Confirm"); message = request.message; prompt.text = ""; prompt.visible = false; break; case JavaScriptDialogRequest.DialogTypePrompt: title = qsTr("Prompt"); message = request.message; prompt.text = request.defaultText; prompt.visible = true; break; } } }
On component completion, we customize the form based on the request type. For a JavaScript prompt dialog we use
dialogAccept()
采用
prompt.text
自变量。
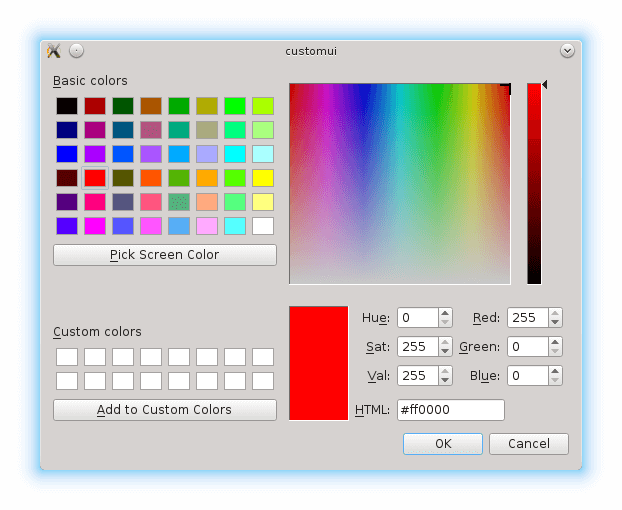
ColorDialogRequest is a request object that is passed as a parameter of the WebEngineView::colorDialogRequested signal:
WebEngineView { ... onColorDialogRequested: function(request) { if (useDefaultDialogs) return; request.accepted = true; openForm({item: Qt.resolvedUrl("forms/ColorPicker.qml"), properties: {"request": request}}); } ... }
使用
onColorDialogRequested
signal handler to check whether we should use the default color picker dialog. If not, we accept the request and switch the view to show the
ColorPickerForm
:
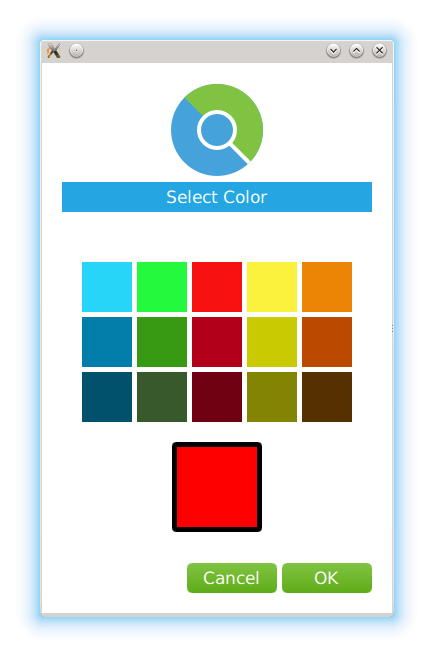
ColorPickerForm { property QtObject request signal closeForm() okButton.onClicked: { request.dialogAccept(colorPicker.color); closeForm(); } cancelButton.onClicked: { request.dialogReject(); closeForm(); } function createCallback(color) { return function() { colorPicker.color = color }; } Component.onCompleted:{ for (var i = 0; i < grid.children.length; i++) { var cell = grid.children[i]; cell.clicked.connect(createCallback(cell.color)); } colorPicker.color = request.color; } }
On component completion, we create callbacks for all the color cells. When the user selects the color and clicks
OK
, we pass the selected color to the
dialogAccept()
方法。
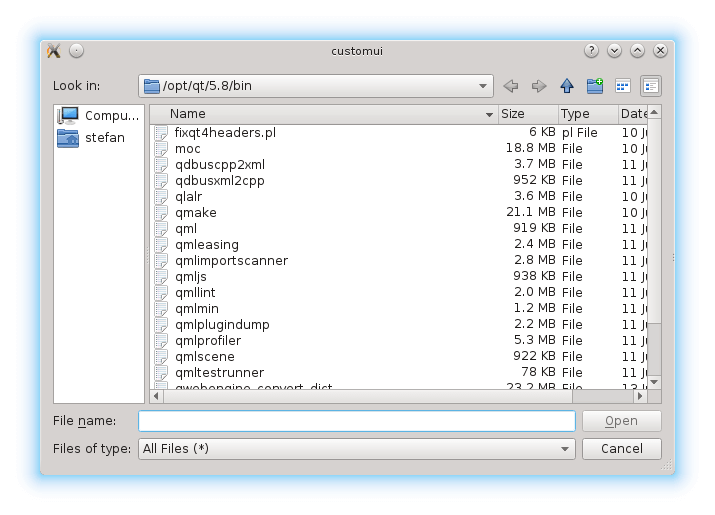
FileDialogRequest is a request object that is passed as a parameter of the WebEngineView::fileDialogRequested signal:
WebEngineView { ... onFileDialogRequested: function(request) { if (useDefaultDialogs) return; request.accepted = true; openForm({item: Qt.resolvedUrl("forms/FilePicker.qml"), properties: {"request": request}}); } ... }
使用
onFileDialogRequested
signal handler to check whether we should use the default color picker dialog. If not, we accept the request and switch the view to show the
FilePickerForm
:
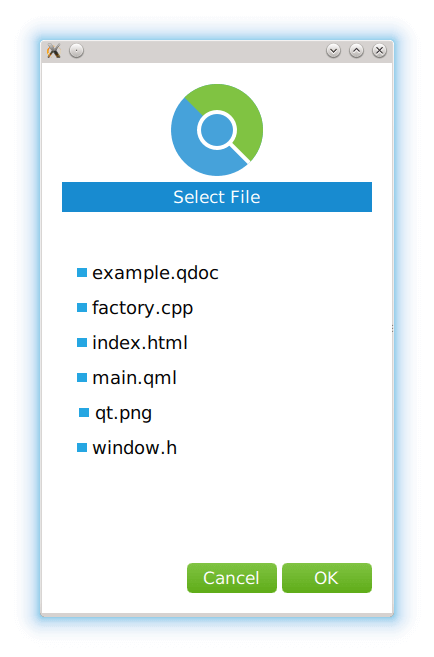
FilePickerForm { property QtObject request property string selectedFile signal closeForm() cancelButton.onClicked: { request.dialogReject(); closeForm(); } okButton.onClicked: { request.dialogAccept('/' + selectedFile); closeForm(); } function createCallback(fileIndex) { return function() { for (var i = 0; i < files.children.length; i++) { var file = files.children[i]; if (i === fileIndex) { selectedFile = file.text; file.selected = true; } else { file.selected = false; } } } } Component.onCompleted: { selectedFile = request.defaultFileName; for (var i = 0; i < files.children.length; i++) { var file = files.children[i]; file.clicked.connect(createCallback(i)); if (file.text === selectedFile) file.selected = true; } }
On component completion, we create callbacks for selecting files. When the user selects a file and clicks
OK
, we pass the selected file to the
dialogAccept
方法。

FormValidationMessageRequest is a request object that is passed as a parameter of the WebEngineView::formValidationMessageRequested signal:
WebEngineView { url: "qrc:/index.html" ... onFormValidationMessageRequested: function(request) { switch (request.type) { case FormValidationMessageRequest.Show: if (useDefaultDialogs) return; request.accepted = true; validationMessage.text = request.text; validationMessage.y = request.anchor.y + request.anchor.height + 10; validationMessage.visible = true; break; case FormValidationMessageRequest.Move: break; case FormValidationMessageRequest.Hide: validationMessage.visible = false; break; } } MessageRectangle { id: validationMessage z: 1 } }
使用
onFormValidationMessageRequested
signal handler to check whether we should use the default message bubble. If not, we accept the request and customize
validationMessage
. Depending on the type of the request, we show, move, or hide the message.
文件: