要运行范例从 Qt Creator ,打开 欢迎 模式,然后选择范例从 范例 。更多信息,拜访 构建和运行范例 .
We begin with a chart that has a spline series and a scatter series with random data. Both series use the same axes.
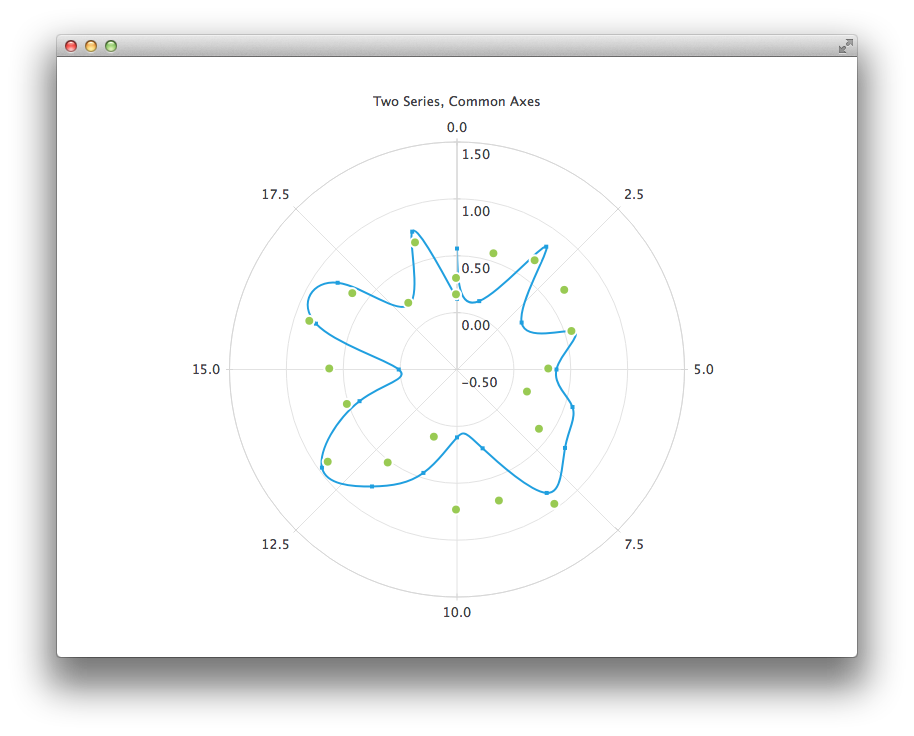
PolarChartView { title: "Two Series, Common Axes" anchors.fill: parent legend.visible: false antialiasing: true ValueAxis { id: axisAngular min: 0 max: 20 tickCount: 9 } ValueAxis { id: axisRadial min: -0.5 max: 1.5 } SplineSeries { id: series1 axisAngular: axisAngular axisRadial: axisRadial pointsVisible: true } ScatterSeries { id: series2 axisAngular: axisAngular axisRadial: axisRadial markerSize: 10 } } // Add data dynamically to the series Component.onCompleted: { for (var i = 0; i <= 20; i++) { series1.append(i, Math.random()); series2.append(i, Math.random()); } }
The next example shows a chart with some accurate historical data for which we need to use a DateTimeAxis 和 AreaSeries .
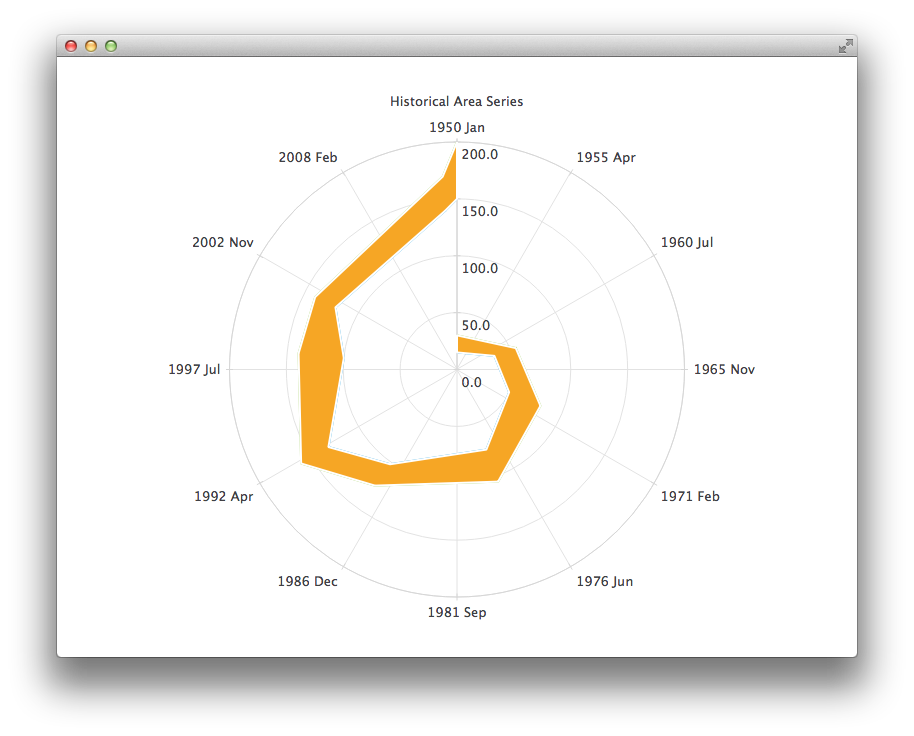
PolarChartView { title: "Historical Area Series" anchors.fill: parent legend.visible: false antialiasing: true DateTimeAxis { id: axis1 format: "yyyy MMM" tickCount: 13 } ValueAxis { id: axis2 } LineSeries { id: lowerLine axisAngular: axis1 axisRadial: axis2 // Please note that month in JavaScript months are zero based, so 2 means March XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1950, 0, 1)); y: 15 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1962, 4, 1)); y: 35 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1970, 0, 1)); y: 50 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1978, 2, 1)); y: 75 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1987, 11, 1)); y: 102 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1992, 1, 1)); y: 132 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1998, 7, 1)); y: 100 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(2002, 4, 1)); y: 120 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(2012, 8, 1)); y: 140 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(2013, 5, 1)); y: 150 } } LineSeries { id: upperLine axisAngular: axis1 axisRadial: axis2 // Please note that month in JavaScript months are zero based, so 2 means March XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1950, 0, 1)); y: 30 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1962, 4, 1)); y: 55 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1970, 0, 1)); y: 80 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1978, 2, 1)); y: 105 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1987, 11, 1)); y: 125 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1992, 1, 1)); y: 160 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(1998, 7, 1)); y: 140 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(2002, 4, 1)); y: 140 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(2012, 8, 1)); y: 170 } XYPoint { x: toMsecsSinceEpoch(new Date(2013, 5, 1)); y: 200 } } AreaSeries { axisAngular: axis1 axisRadial: axis2 lowerSeries: lowerLine upperSeries: upperLine } } // DateTimeAxis is based on QDateTimes so we must convert our JavaScript dates to // milliseconds since epoch to make them match the DateTimeAxis values function toMsecsSinceEpoch(date) { var msecs = date.getTime(); return msecs; }
And the final example with a chart that uses a CategoryAxis to make the data easier to understand.
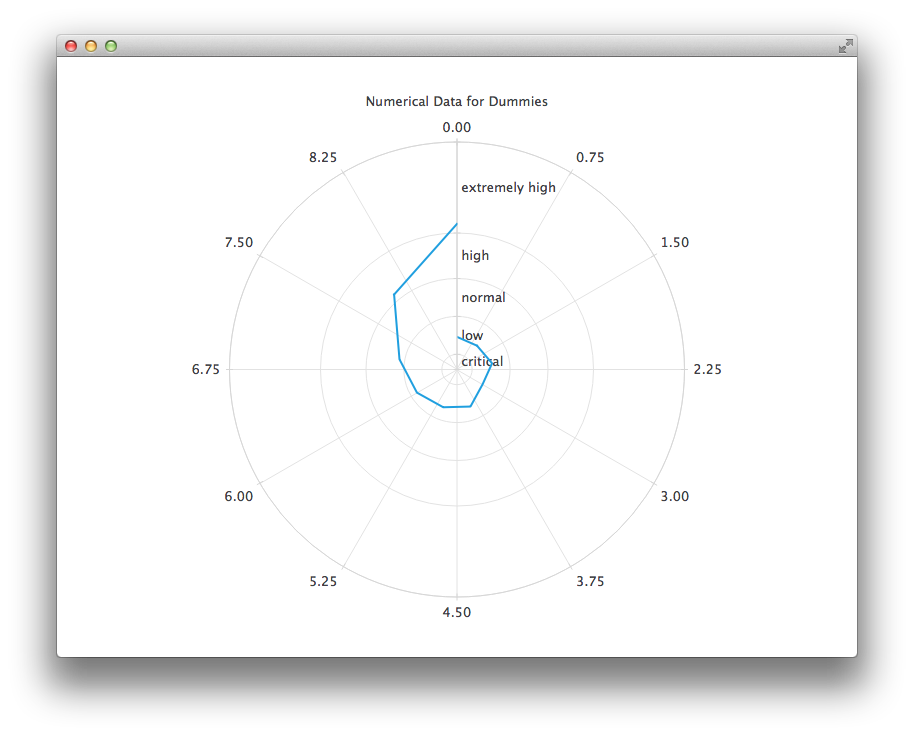
PolarChartView { title: "Numerical Data for Dummies" anchors.fill: parent legend.visible: false antialiasing: true LineSeries { axisRadial: CategoryAxis { min: 0 max: 30 CategoryRange { label: "critical" endValue: 2 } CategoryRange { label: "low" endValue: 7 } CategoryRange { label: "normal" endValue: 12 } CategoryRange { label: "high" endValue: 18 } CategoryRange { label: "extremely high" endValue: 30 } } axisAngular: ValueAxis { tickCount: 13 } XYPoint { x: 0; y: 4.3 } XYPoint { x: 1; y: 4.1 } XYPoint { x: 2; y: 4.7 } XYPoint { x: 3; y: 3.9 } XYPoint { x: 4; y: 5.2 } XYPoint { x: 5; y: 5.3 } XYPoint { x: 6; y: 6.1 } XYPoint { x: 7; y: 7.7 } XYPoint { x: 8; y: 12.9 } XYPoint { x: 9; y: 19.2 } } }
文件: